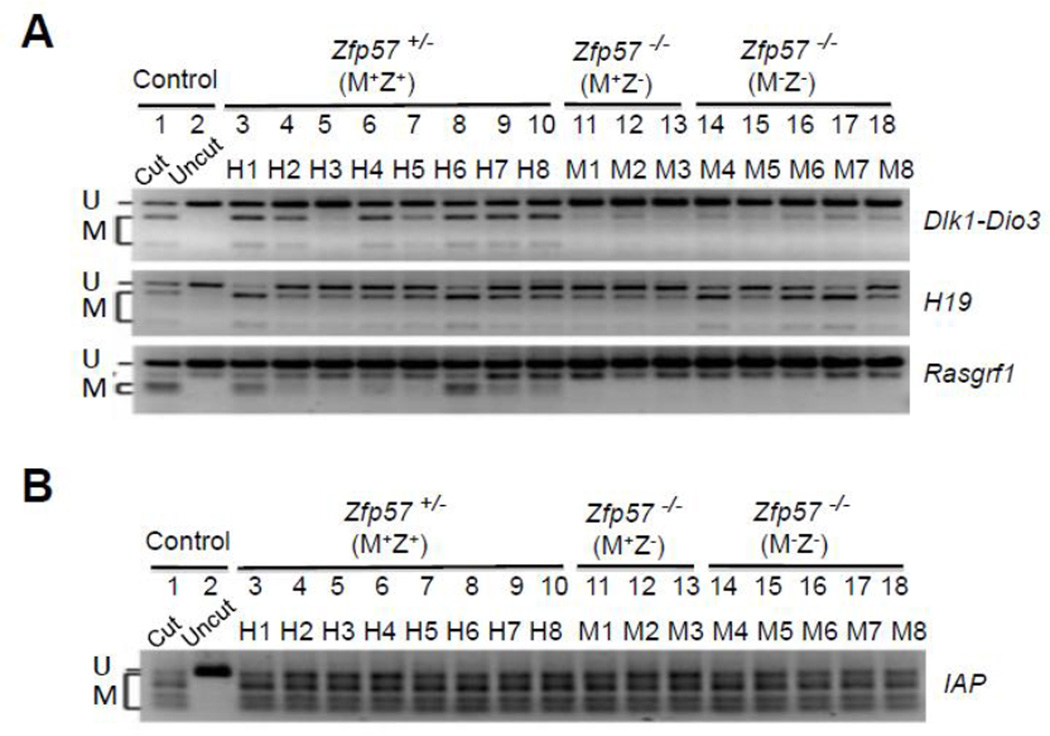
Figure 4. COBRA analysis of paternally inherited DNA methylation imprint.
Restriction enzyme (RE) digestion was performed for the bisulphite PCR product of all ES samples, and “Cut” (Lane 1) but not “Uncut” (Lane 2) control wild-type mouse tail DNA sample. U and M, unmethylated (U) and methylated (M) product after RE digestion, respectively. Lanes 3–10, eight Zfp57+/− (M+Z+) ES clones derived from the blastocysts generated from the cross between Zfp57+/− heterozygous female mice and Zfp57−/− homozygous male mice. Lanes 11–13, three Zfp57−/− (M+Z−) ES clones derived from the blastocysts generated from the cross between Zfp57+/− heterozygous female mice and Zfp57−/− homozygous male mice. Lanes 14–18, five Zfp57−/− (M−Z−) ES clones derived from the cross between Zfp57−/− homozygous female mice and Zfp57−/− homozygous male mice.
A, COBRA analysis was carried out at the IG-DMR of the Dlk1-Dio3 imprinted region, H19 DMR of the Igf2-H19 imprinted region and Rasgrf1 DMR.
B, COBRA analysis of the IAP repeats.