Abstract
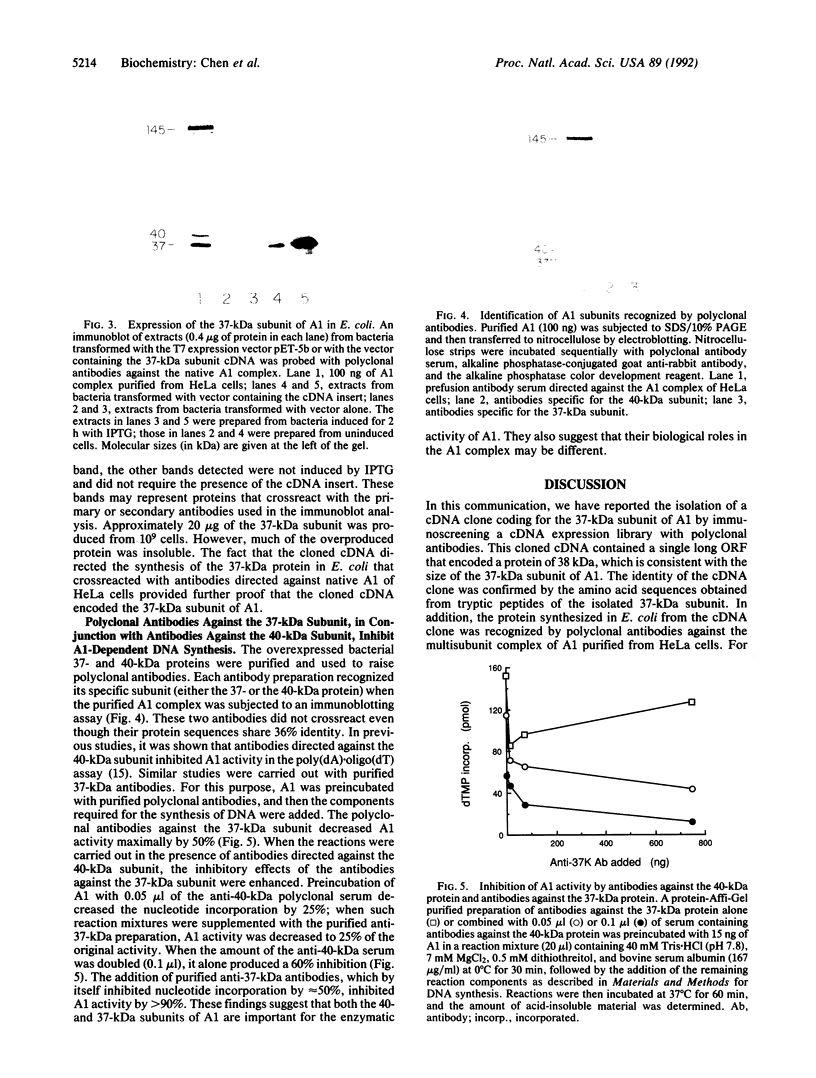
The elongation of primed DNA templates by DNA polymerase delta and DNA polymerase epsilon requires the action of two accessory proteins, proliferating cell nuclear antigen and activator 1 (A1, also called replication factor C). A1 is an enzyme that contains five different subunits (145, 40, 38, 37, and 36.5 kDa). In this paper, we describe the isolation of the gene encoding the 37-kDa subunit from HeLa cells. This gene was cloned, sequenced, and overexpressed in Escherichia coli. The amino acid sequence shows a high degree of homology to the 40-kDa subunit of A1; they both contain the identical ATP-binding motif, but in contrast to the bacterial expressed 40-kDa protein, the 37-kDa expressed protein did not bind ATP. Both the 37- and 40-kDa proteins share substantial homology with the phage T4 gene 44 protein and to a lesser extent with the tau and gamma subunits of the E. coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. Polyclonal antibodies against the bacterially expressed 37- and 40-kDa proteins do not crossreact and are specific in their interaction. Antibodies against the 37-kDa protein maximally inhibited (by 50%) the A1-dependent synthesis of DNA by DNA polymerase delta; antibodies against the 40-kDa protein quantitatively inhibited the same reaction. When A1-dependent synthesis of DNA was partially inhibited by antibodies against the 40-kDa subunit, the addition of antibodies against the 37-kDa subunit inhibited DNA synthesis to a greater extent than the anti-37-kDa antibody alone. These results suggest that both the 37- and 40-kDa subunits of A1 are required for the biological role of A1 and that they may function differently in this process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Barry J., Bedinger P., Formosa T., Jongeneel C. V., Kreuzer K. N. Studies on DNA replication in the bacteriophage T4 in vitro system. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):655–668. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Pan Z. Q., Hurwitz J. Sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of the 40-kDa subunit of activator 1 (replication factor C) of HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2516–2520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Horiuchi K., Zinder N. D. The functional origin of bacteriophage f1 DNA replication. Its signals and domains. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):507–521. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J., Dean F. B., Kwong A. D., Lee S. H. The in vitro replication of DNA containing the SV40 origin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18043–18046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Eki T., Hurwitz J. Synthesis of DNA containing the simian virus 40 origin of replication by the combined action of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7361–7365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Mechanism of elongation of primed DNA by DNA polymerase delta, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and activator 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5672–5676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Ishimi Y., Kenny M. K., Bullock P., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. An inhibitor of the in vitro elongation reaction of simian virus 40 DNA replication is overcome by proliferating-cell nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9469–9473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C., Walker J. R. Relation of the Escherichia coli dnaX gene to its two products--the tau and gamma subunits of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7663–7675. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Kwong A. D., Ishimi Y., Hurwitz J. Studies on the DNA elongation inhibitor and its proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent control in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4877–4881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Kwong A. D., Pan Z. Q., Hurwitz J. Studies on the activator 1 protein complex, an accessory factor for proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent DNA polymerase delta. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):594–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Pan Z. Q., Kwong A. D., Burgers P. M., Hurwitz J. Synthesis of DNA by DNA polymerase epsilon in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22707–22717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Kallen R. G., Alberta B. M. Analysis of a T4 DNA replication protein complex. Studies of the DNA recognition site for T4 gene 44/62 and 45 protein-catalyzed ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):5180–5185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Nossal N. G., Williams K. R. Bacteriophage T4 gene 44 DNA polymerase accessory protein. Sequences of gene 44 and its protein product. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15425–15432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Melendy T., Stillman B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):534–539. doi: 10.1038/346534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Functions of replication factor C and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen: functional similarity of DNA polymerase accessory proteins from human cells and bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1023–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Multiple replication factors augment DNA synthesis by the two eukaryotic DNA polymerases, alpha and delta. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3883–3889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08567.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Purification of a cellular replication factor, RF-C, that is required for coordinated synthesis of leading and lagging strands during simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):609–619. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Replication factors required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. I. DNA structure-specific recognition of a primer-template junction by eukaryotic DNA polymerases and their accessory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1950–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





