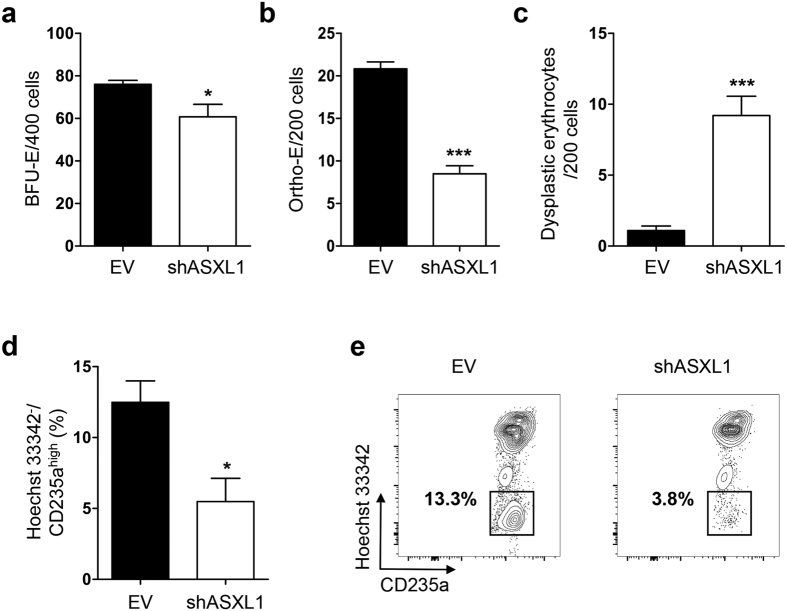
Figure 2. Knockdown of ASXL1 in CB CD34+ cells impairs their erythroid differentiation.
(a) CB CD34+ cells were transduced with lentivirus carrying shASXL1 or empty vector (EV) for 2 days. The sorted GFP+ cells were cultured in methylcellulose for 14 days. The numbers of BFU-E from CB CD34+ cells transduced with shASXL1 were significantly lower than those from EV controls. Data are represented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05. (b,c) May-Giemsa stained cytospin preparation from the cultures of GFP+ CD34+ cells expressing shASXL1 or EV were analyzed on day 12. A quantitative comparison based on the cell counting of different erythroid progenitors and dyserythropoietic cells in 200 cells/field from 10 different fields revealed that cells transduced with shASXL1 contained a lower percentage of Ortho-E (b) and a higher percentage of dyserythropoietic cells (c) compared to the EV. Data are represented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. ***p < 0.001. (d,e) Analysis of erythrocyte enucleation after ASXL1 knockdown. After 10 days of culture in methylcellulose, 5 individual colonies were isolated from ASXL1 knockdown or EV CD34+ cells and seeded in IMDM basic medium supplemented with EPO. After an additional 6 days, the cells were stained with Hoechst 33342, and anti-CD235a antibodies. The percent of Hoechst 33342−/CD235ahigh enucleated erythrocytes were determined. ASXL1-KD cultures contained a decreased proportion of enucleated erythrocytes compared to the EV cultures. Data are represented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05.