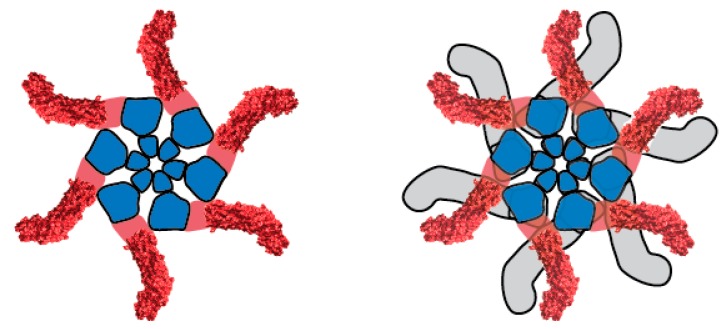
Figure 3.
Structural organization of water-soluble VacA oligomers. A hexamer (left) and dodecamer (right) are shown. Within each component p88 monomer, p33 and p55 domains are shown in blue and red, respectively. A crystal structure has been solved for a portion of p55 [43], corresponding to peripheral elements of the oligomer [54]. Water-soluble hexamers are predicted to be structurally similar to membrane channels formed by VacA.