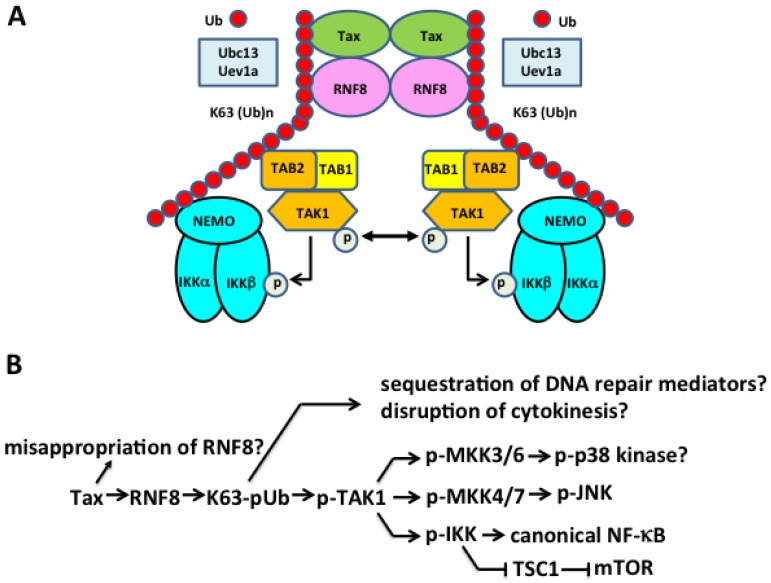
Figure 2.
Tax hijacks the ubiquitin E3 ligase, ring finger protein 8 (RNF8) and E2 conjugating enzyme UBC13: Uev1A/Uev2 to activate transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ)-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), I kappa B kinase (IKK), canonical NF-κB and other signaling pathways. (A) Tax directly interacts with and stimulates RNF8 and Ubc13:Uev1A/2 to assemble long lysine 63-linked polyubiquitin (K63-pUb) chains, which then serve as the signaling scaffolds for K63-pUb-binding TAK1 and IKK to convene and become activated. As NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) interacts weakly with K63-pUb chains, the direct interaction between Tax and NEMO may mediate IKK recruitment to and activation by TAK1. (B) The Tax-RNF8 signaling axis drives increased assembly of K63-linked polyubiquitin chains, which activate TAK1. TAK1, in turn, signals the activation of MKKs and IKK, and downstream p38 kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and the canonical NF-κB pathway. The misappropriation and aberrant activation of RNF8 and the increased assembly of K63-linked polyubiquitin chains may sequester key mediators of DNA damage repair and cytokinesis to induce genomic instability in the forms of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and chromosome aneuploidy.