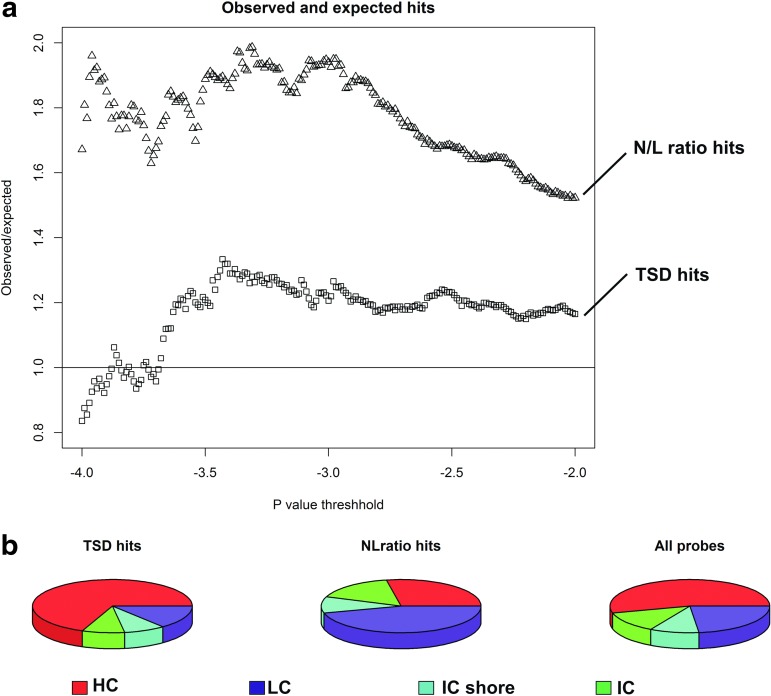
FIG. 2.
Observed and expected number of hits for TSD and the N/L ratio as well as their CpG density distribution: Ratios between observed and expected changes in methylation with dependence on TSD at different p value thresholds (a). The upper line is determined by the number of significant b coefficients from [Eq. 1] and the lower line depends on the number of significant a coefficients. The log (p value) threshold for entry in analysis step II (testing whether an observed methylation change is larger than the median change observed for technical replicates) was defined as 2.5. A total of 652 probes for TSD (coefficient a) and 891 for the N/L ratio (coefficient b) passed this threshold. Distribution of the probes among different CpG density classes (b). HC probes are defined as having a CG base content more than 55%, Obs/Exp CpG ratio more than 0.75, and being longer than 500 bps. The corresponding criteria for IC probes are 50%, 0.48, and 200, respectively, whereas those probes that did not fit either criteria were labeled as LC. ICshore probes are those that are located at the end of an IC-Island (Price, et al., 2013). The left circle diagram represents the distribution of the 652 probes associated with sleep deprivation and the middle diagram shows the N/L ratio-associated probes. The right diagram displays the background distribution of all investigated probes. Chi-squared distribution tests determined that TSD-related probes (probes with significant a coefficients) were more likely to be HC probes. N/L ratio-related probes (probes with significant b coefficients) were more likely to be LC probes. HC, high-density CpG; IC, intermediate-density CpG; ICshore, shore region of intermediate-density islands; LC, low-density CpG; N/L, neutrophil/leukocyte.