Figure 6.
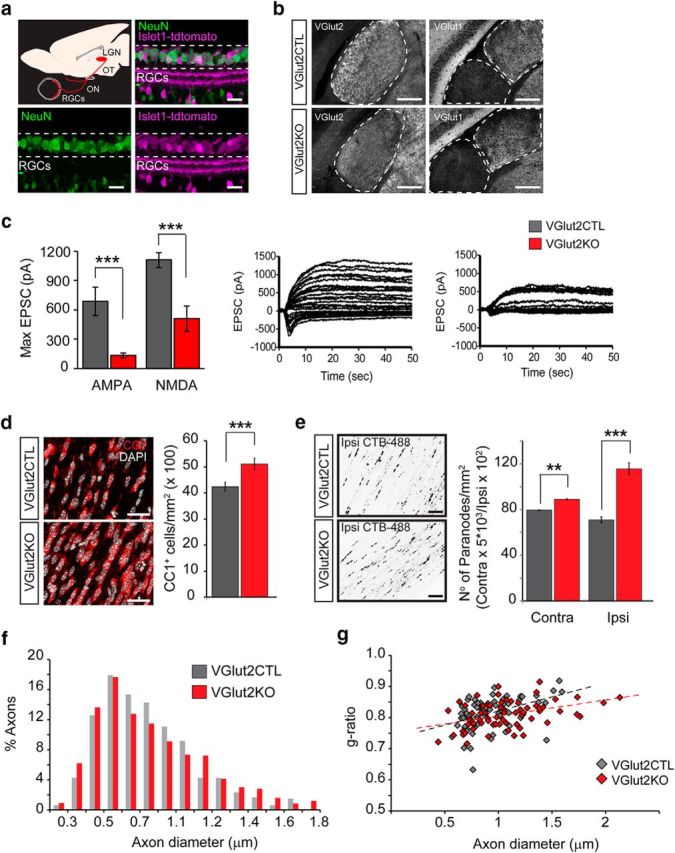
Genetic attenuation of synaptic glutamate release from retinal axons increases oligodendrogenesis and the number of nodes of Ranvier. The VGlut2 gene that mediates the uptake of glutamate into synaptic vesicles was conditionally ablated in RGCs under the control of the Islet1 (Islet-class factor 1) promoter by crossing Islet1-cre mice with floxed VGlut2 mice. a, Retinal section immunostained for NeuN (green) displaying tdTomato cre recombination reporter fluorescence (magenta) in most of the RGCs. Scale bar, 30 μm. b, Left, Sections through the dLGN immunostained for VGlut2 in the conditional VGlut2KO mice (islet1-cre:VGlut2fl/fl) and control littermates. Scale bar, 200 μm. Right, Sections through the dLGN and ventral LGN immunostained for VGlut1. c, Representative postsynaptic currents evoked by stimulation of the OT (at varying intensities), recorded from P9–P12 control and KO mice dLGN neurons. Each set of traces shows the superimposition of two experiments: recordings while holding the postsynaptic cell membrane potential at −70 mV to register mostly AMPAR-mediated responses, and recordings at 40 mV to elicit NMDAR-mediated currents. Maximal currents evoked at saturating stimulation intensity were quantified and displayed in the bar graphs. VGlut2 KO mice exhibited strongly attenuated total synaptic drive through both AMPA (CTL = 688 ± 146 pA; KO = 133 ± 28 pA; p = 0.0002) and NMDA receptors (CTL = 1108 ± 75 pA; KO = 508 ± 128 pA; p = 0.0007). d, Representative images and quantification of the number of CC1+ mature oligodendrocytes in KO and CTL mice (CTL = 42.42 ± 1.68, MD = 51.08 ± 2.19, p = 0.007, t test, n = 3 mice). Scale bar, 30 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. e, The CTB-488 tracer was intravitreally injected in VGlut2KO and control mice to label nodes of Ranvier in RGC axons 1 d before death at P40. The average number of CTB-488+ paranodes in the contralateral and ispsilateral OTs increased after synaptic glutamate reduction (Contra VGlut2CTL = 79.4 ± 0.68, VGlut2KO = 88.97 ± 0.63, p = 0.008 t test; Ipsi VGlut2CTL = 70.97 ± 4.87; VGlut2KO = 115.5 ± 10.23; p = 0.0005, t test, n = 3 mice). f, Axon diameter distribution was analyzed in electron microscopy images of P14 VGlut2KO and control mice ONs (CTL = 0.74 ± 0.01, KO = 0.76 ± 0.01, p = 0.17, t test, n ≥ 475 axons). g, Scatter plots of g-ratio as a function of axon diameter in control and KO mice display no significant difference in myelin thickness (average g-ratio CTL = 0.81; KO = 0.80; p = 0.47, t test, n = 70 axons). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
