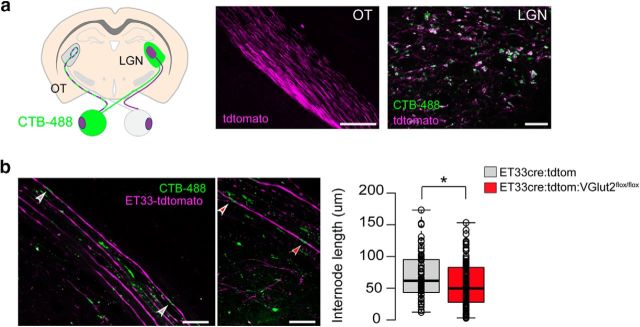
Figure 7.
RGC glutamate neurotransmission regulates internode length. a, Left, Schematic diagram of a coronal brain section depicting sparse colabeling of ipsilateral-projecting RGC axons genetically using the reporter mouse ET33-cre:tdtomato (purple) and upon unilateral injection of the tracer cholera toxin B conjugated with AlexaFluor-488 (CTB-488, green). Right, Representative images of the ET33-cre:tdtomato mice showing the genetically labeled OT (scale bar, 400 μm) and colocalization of the reporter and the tracer in RGC axon terminals at the LGN (scale bar, 20 μm). b, Left, Representative merged images showing genetically labeled axons (ET33-cre:tdtomato) and CTB-labeled nodes of Ranvier in the OT. Myelin internode lengths were measured as the distance between two CTB-labeled nodes (arrowheads) in ET33-tdtomato axons. Scale bar, 20 μm. Right, Box-plot of internode lengths measured from control ET33-cre:tdtomato mice and after conditionally ablating VGlut2 from ET33-cre:tdtomato-expressing neurons (ET33-cre:tdtomato:VGlut2fl/fl) at P20–P40. Center lines indicate the medians (CTL = 74.39 μm n = 221 internodes from 8 mice; MD = 63.55 μm n = 116 internodes from 7 mice; p = 0.029 by Mann–Whitney U test). Box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles. Whiskers extend to 5th and 95th percentile (Altman). Dots indicate outliers. Open circles represent data points. *p < 0.05.