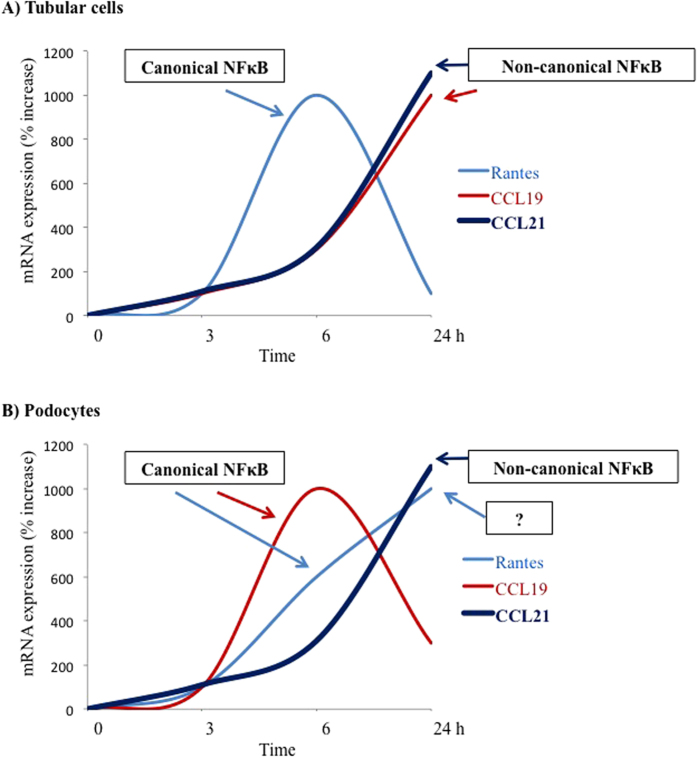
Figure 7. Differential involvement of NFκB activation pathways in the regulation of chemokine expression in renal tubular cells and podocytes.
In splenocytes, both CCL19 and CCL21 are transcriptional targets of the non-canonical pathway for NFκB activation involving NFκB2/RelB heterodimers18. (A) Murine renal tubular cells15,17. TWEAK-induced RANTES expression is inhibited by parthenolide, suggesting canonical NFκB activation. By contrast, CCL21 expression is prevented by NIK siRNA, but not by parthenolide. While not specifically studied by functional inhibitors, the time-course of CCL19 expression and the fact that CCL19 was upregulated by TWEAK but not by TNF suggests that CCL19 is a transcriptional target for non-canonical NFκB activation in tubular cells. (B) Podocytes. Note the different time-course of TWEAK-induced RANTES and CCL19 mRNA expression between tubular cells and podocytes. The increased CCL19 mRNA and the early increase in RANTES mRNA is inhibited by parthenolide, suggesting dependence on canonical NFκB activation. CCL21 is the only chemokine that depends on non-canonical NFκB activation in splenocytes, tubular cells and podocytes. The late increase of RANTES mRNA expression in podocytes could not be inhibited by targeting the canonical or non-canonical pathways suggesting NFκB-independence or activation of alternative NFκB pathways13,15.