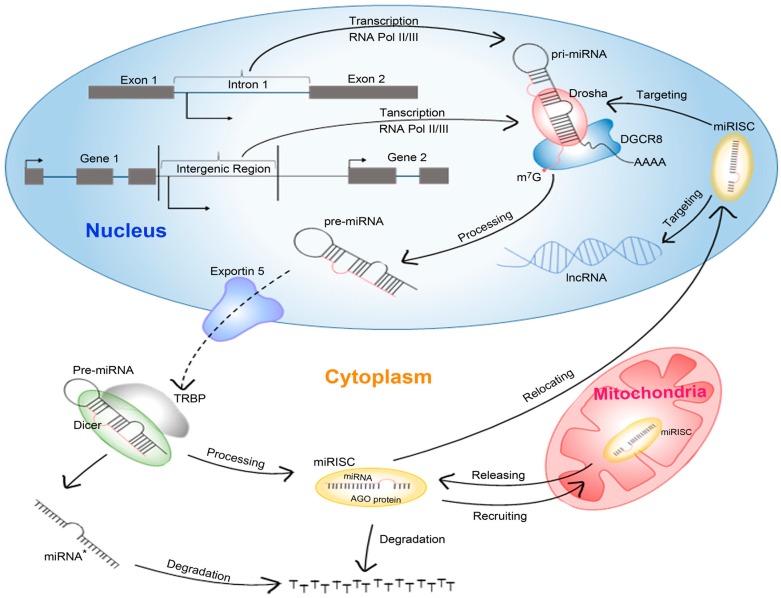
Figure 1.
miRNA biogenesis and action. Pri-miRNA is typically transcribed from intron or intergenic region by polymerase II or polymerase III (Pol II or Pol III). In the nucleus the pri-miRNA is recognized and cleaved by Drosha and its partner DGCR8 to generate the ~70 nucleotides of pre-miRNA. The nuclear export of pre-miRNA molecules into the cytoplasm is mediated by Exportin 5 (XPO5) where they are further processed by Dicer with the aid of TAR RNA binding protein (TRBP) to generate the duplex of miRNA:miRNA*. Generally, the miRNA* is released to be degraded, while the miRNA is loaded into Agronaute (AGO) protein to form the miRNA-induced silencing complexes (miRISC) which could regulate the gene expression post-transcriptionally. When the target mRNAs are unavailable, the miRNA would also decay after being released from the miRISC. In some cases, the miRISC is recruited to mitochondria or relocated to nucleus, at which it can target diverse targets including pri-miRNAs and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs).