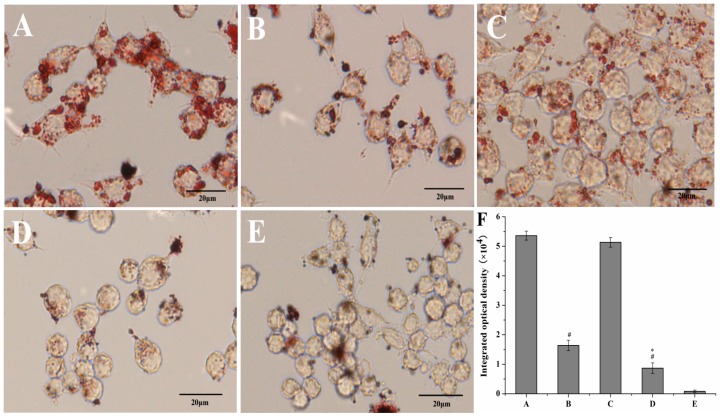
Figure 9.
Oil Red O staining and integrated optical density of oxLDL-induced macrophages. (A) positive control group; (B) curcumin solutions; (C) blank PS-containing carriers; (D) Cur-mNLCs; (E) negative control group; (F) integrated optical density analysis; # p < 0.01, compared with A, * p < 0.05, compared with B. In panel F, the letters of A–E in the X axis correspond to Group A–E, respectively. Curcumin solutions or Cur-mNLCs markedly reduced oxLDL-induced cholesterol accumulation in macrophages (p < 0.01 for Group B or D vs. Group A), and Cur-mNLCs exhibited more potent effects than curcumin solutions (p < 0.05 for Group D vs. Group B). PS did not have an obvious effect on macrophages’ lipid uptake behavior (p > 0.05 for Group C vs. Group A) (mean ± SD, n = 6). Scale bar is 20 µm.