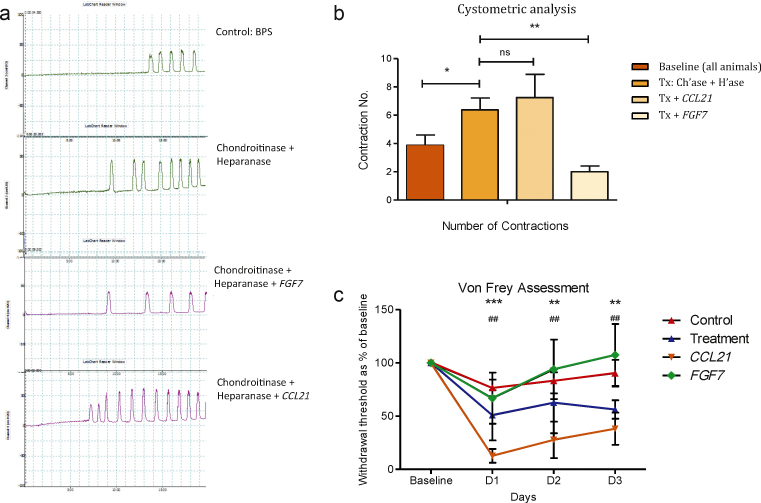
Fig. 5.
Cystometry and behaviour assessment. (A) Representative cystometric recordings of bladders, showing contraction frequency following baseline assessment, enzymatic proteoglycan deglycosylation, FGF7 treatment, and CCL21 treatment in permeabilised bladders. (B) Quantification of the cystometric number of bladder contractions. Displayed is the mean total number of contractions in a 20-min interval ±1 standard error of the mean (SEM; five rats per group). Statistical significance calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni post-test correction. (C) Behavioural assessment. Each point represents the mean mechanical withdrawal threshold as a percentage of baseline ±1 SEM (five rats per group). Statistical significance was calculated using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. The CCL21 treatment withdrawal threshold is significantly lower than the control group and animals’ postenzymatic deglycosylation alone.
BPS = bladder pain syndrome; Ch’ase = chondroitinase; H’ase = heparanase; ns = not significant; Tx = treatment.
(B) * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. (C) * Significance difference in CCL21 from baseline: *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; # significance difference in treatment from baseline: ##p < 0.01.