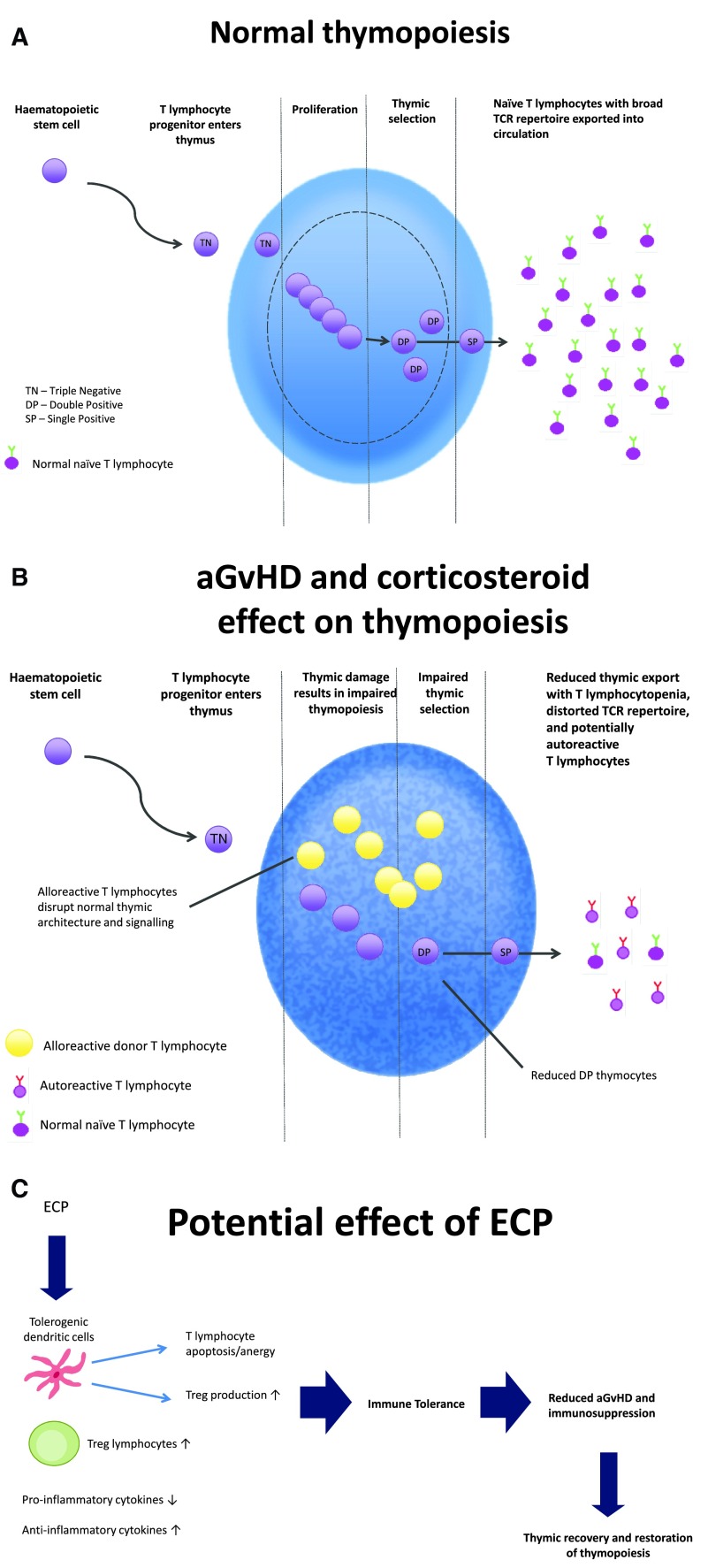
Figure 1. Normal thymopoiesis, effect of acute graft-versus-host disease (aGvHD) and corticosteroids on thymic function, and the potential effect of extracorporeal photopheresis (ECP) allowing thymic recovery.
Thymic damage occurs secondary to allogeneic T lymphocytotoxicity during aGvHD, corticosteroid-mediated damage, and other non-selective T lymphocyte-suppressive agents used in the treatment of aGvHD, causing impaired thymopoiesis ( A), with reduced thymic export and a distorted T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire with potentially autoreactive thymocytes escaping negative selection ( B). ECP, by promoting immune tolerance and enabling reduction and cessation of conventional immunosuppression, may allow thymic recovery, resumption of normal thymopoiesis, and complete and long-lasting immunoreconstitution post-haematopoietic stem cell transplantation ( C). Abbreviations: Treg, regulatory T lymphocyte; DP, double positive.