Figure 6.
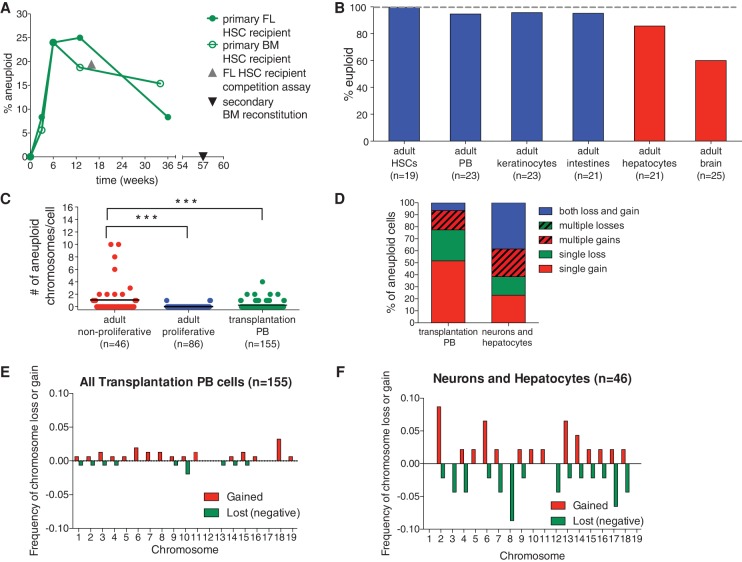
Bub1bH/H adult regenerative tissues show evidence of selection against aneuploid cells. (A) The percent aneuploidy over time during hematopoietic reconstitution with Bub1bH/H HSCs was determined by single-cell sequencing of peripheral blood cells derived from primary recipient mice of Bub1bH/H bone marrow (open circles) or Bub1bH/H fetal liver (closed circles) cells at the indicated times after transfer. Peripheral blood cells from a mouse reconstituted with Bub1bH/H FL-HSCs 16 wk after competitive reconstitution (shown as the percent of total peripheral blood; gray triangle) (Fig. 1G) and from a Bub1bH/H secondary bone marrow recipient mouse (black triangle) (Fig. 5C) were also sequenced. Baseline aneuploidy was determined by single-cell sequencing of FL-HSCs and BM-HSCs. Segmentation plots of all sequenced cells are shown in Supplemental Figures S7 and S8. (B) Percentage of euploid cells found in different adult Bub1bH/H cell types. BM-HSCs, peripheral blood cells (PB), keratinocytes, and intestines (in blue) are from ∼4-mo-old Bub1bH/H mice. Data from hepatocytes and brains (in red) are from Knouse et al. (2014) and ∼6-mo-old Bub1bH/H mice. Segmentation plots of all newly sequenced cells are shown in Supplemental Figure S9. (C) The number of aneuploid chromosomes per cell in all adult cells analyzed in A and B. The bar represents the mean value for each population. t-tests were performed for significance. (***) P < 0.001. (D) Summary of chromosome gain and loss events observed in each cell from transplantation peripheral blood cells and adult nonproliferative neurons and hepatocytes. “Multiple gains” and “multiple losses” describe cells that have gained or lost two or more chromosomes. “Both loss and gain” describes cells that have gained at least one chromosome and lost at least one chromosome. (E,F) Frequency of chromosome gain (red) or chromosome loss (green) by chromosome observed in all peripheral blood cells after transplantation (E) and in all adult neurons and hepatocytes (F).