FIGURE 2:
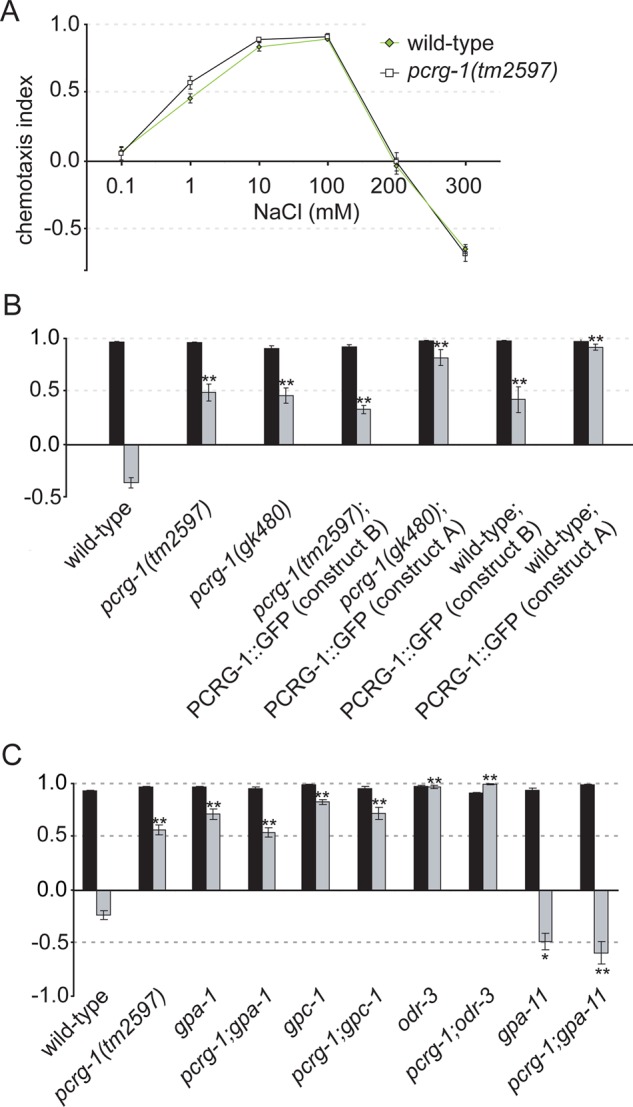
pcrg-1 animals show a defect in behavioral plasticity. (A) Naive responses to NaCl are not affected in pcrg-1 animals. Chemotaxis responses of wild-type (black line) and pcrg-1(tm2597) (green line) animals to various concentrations of NaCl. (B) Mutation of pcrg-1 affects gustatory plasticity. Worms are washed for 15 min in a low-salt buffer (black bars) or a buffer containing 100 mM NaCl (gray bars) and tested for chemotaxis to 25 mM NaCl. Wild-type animals show avoidance of NaCl after preexposure, whereas the two pcrg-1 mutants and the two transgenic strains carrying extra copies of pcrg-1 remain attracted to NaCl. **Statistically significantly different compared with wild type (p < 0.001). (C) pcrg-1 interacts with G-protein signal transduction in gustatory plasticity. Worms are washed for 15 min in a low-salt buffer (black bars) or a buffer containing 100 mM NaCl (gray bars) and tested for chemotaxis to 25 mM NaCl. *, Statistically significantly different compared to wild type (p < 0.05). **, Statistically significantly different compared to wild type (p < 0.001). Comparisons were also performed between double mutants and their corresponding single mutants. The only statistically significantly differences (p < 0.001) were between pcrg-1 and odr-3, pcrg-1 and pcrg-1;odr-3, pcrg-1, and gpa-11, and pcrg-1 and pcrg-1;gpa-11. Means + SEM; n > 100 for all assays.
