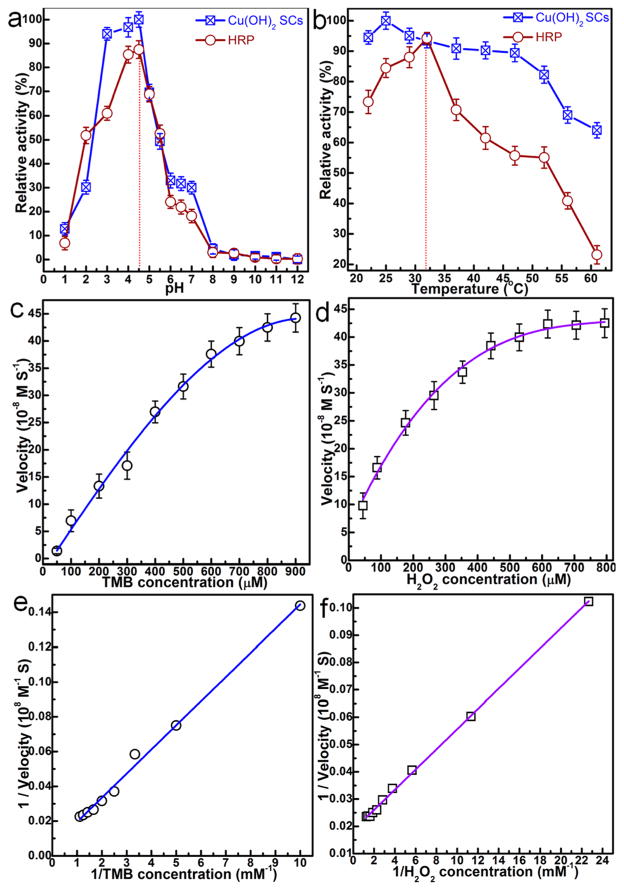
Figure 6.
(a and b) pH- and temperature-dependent peroxidase-mimic activity of Cu(OH)2 SCs and HRP. (a) Cu(OH)2 SCs and HRP show an optimal pH of 4.5; (b) Cu(OH)2 SCs and HRP show an optimal temperature around 25 and 32 °C, respectively. Experiments were carried out using 30 μg of SCs or 300 ng of HRP in a reaction volume of 0.5 mL of 0.2 M NaAc buffer, with 800 μM TMB as substrate. H2O2 concentration was 530 μM for SCs and HRP. The maximum point in each curve (a and b) was set as 100%. Steady-state kinetic assays and catalytic mechanism of Cu(OH)2 SCs were carried out under the following conditions: (c) The concentration of H2O2 was 530 μM, and TMB concentration was varied. (d) The concentration of TMB was 800 μM, and H2O2 concentration was varied. (e and f) Double reciprocal plots for Cu(OH)2 SCs with the concentrations of (e) H2O2 fixed and TMB varied and (f) TMB fixed and H2O2 varied.