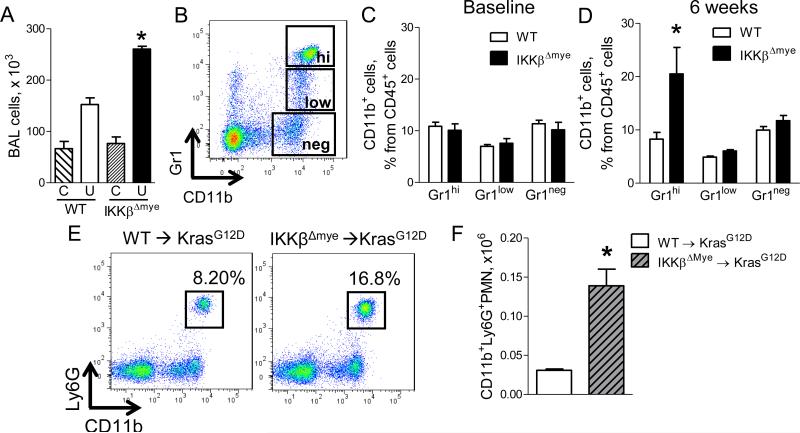
Figure 2.
Neutrophils are increased in the lungs of mice lacking myeloid NF-κB signaling. A) Number of total BAL cells in WT and IKKβΔmye mice at baseline (C) and at 6 weeks after urethane injection (U) (n=7-9 mice per group; *p < 0.05 compared with urethane-treated WT mice). B) Representative FACS plots and (C-D) Percentages of viable CD45+/CD11b+/Gr1hi neutrophils (Gr1hi), CD45+/CD11b+/Gr1low monocytes (Gr1low), and CD45+/CD11b+/Gr1neg macrophages (Gr1neg) in the lungs of WT and IKKβΔmye mice at (C) baseline and (D) 6 weeks after urethane injection (n=4-11 mice per group; *p < 0.05 compared with WT). E) Representative FACS plots and (F) total viable CD45+/CD11b+/Ly6G+ neutrophils in the lungs of WT→KrasG12D and IKKβΔmye→KrasG12D mice 8 weeks after adeno-Cre (n=4 mice per group; *p < 0.05 compared with WT→KrasG12D). Ly6G identifies the granulocytic subgroup of the Gr1 marker. See also Figure S2.