Fig.2.
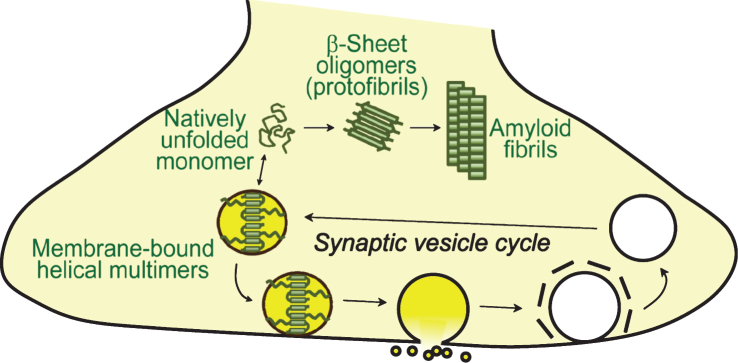
Physiological and pathological conformations of α-synuclein at the synapse. Cytosolic α-synuclein is monomeric and natively unfolded. Upon binding to synaptic vesicles, the N-terminal residues of α-synuclein adopt a helical structure. Membrane binding of α-synuclein is associated with its multimerization, which is essential for its physiological function at the synapse. Pathologically, unfolded α-synuclein in the cytosol can convert into β-sheet containing oligomers (protofibrils) which eventually form amyloid fibrils.