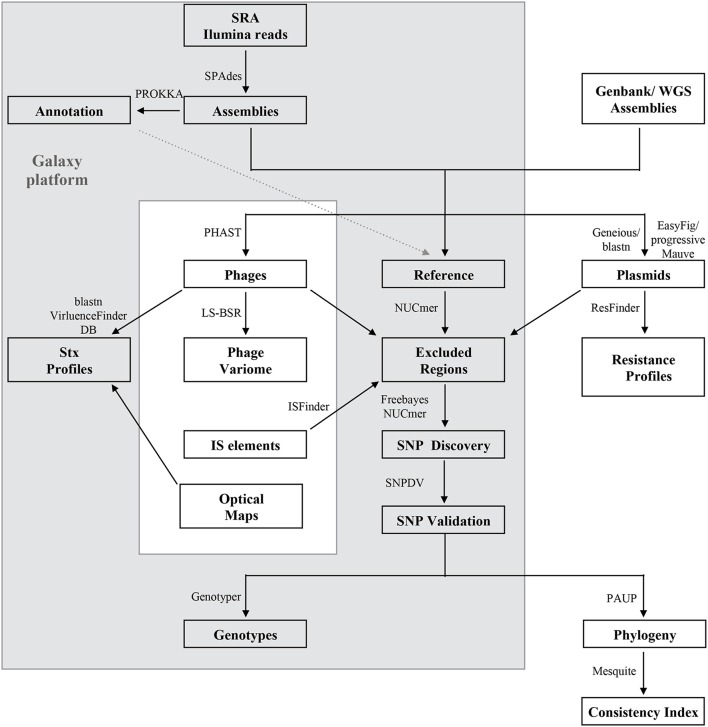
Figure 1.
Bioinformatics analyses of the E. coli O157:H7 core and mobile genome. The majority of the analyses were performed on Galaxy (Goecks et al., 2010), an open-source web-based bioinformatics platform (gray box). Illumina reads, draft or closed genomes were retrieved from the NCBI SRA or WGS sequence repositories (Supplemental Table 1). Reads were assembled with SPAdes v 3.5.0 (Bankevich et al., 2012), and annotated with PROKKA v 1.11.0 (Seemann, 2014). A reference genome was selected for each outbreak analysis and distinct regions were excluded from SNP validation as follows: Repeats with NUCmer (Delcher et al., 2003), phages with PHAST (Zhou et al., 2011) plasmids by querying against a custom E. coli plasmid database and IS elements from ISFinder (Siguier et al., 2006). Optical maps were generated to facilitate accurate prophage and mobilome profiling (Eppinger et al., 2011b). Read based SNP discovery was based on Bowtie2 alignment (Langmead and Salzberg, 2012) and subsequent Freebayes SNP calling (Garrison and Marth, 2012) and for closed or draft genomes on NUCmer (Delcher et al., 2003), followed by blast- and PCR-based SNPs validations to curate for false-positives with strategies detailed in (Eppinger et al., 2011b, 2014). The identified SNPs were genotyped and used for phylogenetic reconstruction by maximum parsimony of the outbreaks with PAUP v4.0a146 (Wilgenbusch and Swofford, 2003). Consistency index and majority consensus trees were built with Mesquite (Maddison and Maddison, 2015). The mobilome was analyzed in regards to phage content with large scale-blast score ratio (LS-BSR) (Sahl et al., 2014) and computed matrices visualized with MeV (Saeed et al., 2003). Shiga toxins were identified by discontiguous megablast (Buhler, 2001; Ma et al., 2002) against the VirulenceFinder (Joensen et al., 2014) database. Plasmids were identified after alignment of draft genomes to the closest closed reference plasmid in Geneious (vR9) (Kearse et al., 2012). Unmapped remaining contigs were queried against NCBI nr plasmids by discontiguous megablast (Buhler, 2001; Ma et al., 2002). Identified plasmid homologs were compared and visualized with EasyFig (Sullivan et al., 2011) by tblastx (Altschul et al., 1990) or progressiveMauve (Darling et al., 2010). Plasmids and chromosomes were further surveyed for presence of resistance loci using ResFinder (Kleinheinz et al., 2014).