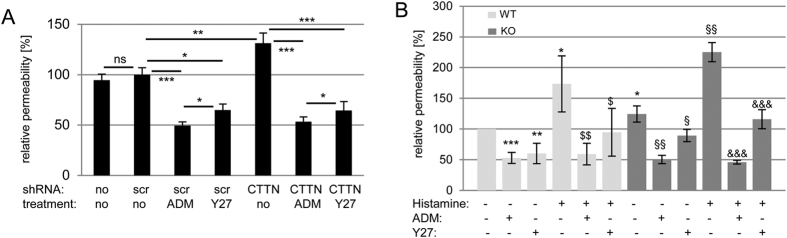
Figure 6. Adrenomedullin administration and ROCK1 inhibition rescue the increase in endothelial permeability provoked by the loss of cortactin.
(A) HMEC-1 monolayers were cultured on 0.4 μm transwell filters until confluent. Fresh medium was added to the upper and lower chambers. Cells were untreated or treated for 1 h with 100 nM ADM or 10 μM Y-27632. Then, 150 kDa FITC-dextran was added to the upper chamber and incubated for 30 min. 100 μl were collected from the lower chamber and signal intensity was measured using a fluorometer. Data are mean +/−SDM of three independent experiments and represent relative permeability with control cells expressing scrambled (scr) shRNA set to 100%. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. (B) Miles assays to determine vascular permeability in the skin were performed as described in Methods with the indicated treatments. WT: n = 8; KO: n = 5 from 2 independent experiments. Data are presented as relative permeability with the untreated WT control group set to 100%. Statistical analysis was performed by One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. *p vs WT ctrl; $p vs. WT + histamine; §p vs. KO ctrl; &p vs. KO + histamine; three symbols: p < 0.001, two symbols: p < 0.01; one symbol: p < 0.05.