Fig. 4.
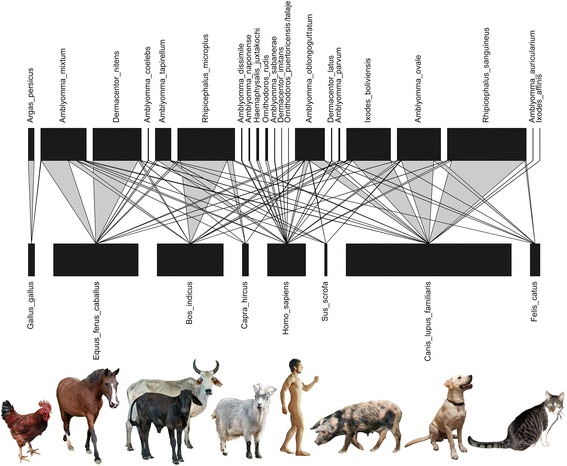
Host associations of ticks with domestic animals and humans, visualized by a bipartite network. Nodes (black) represent species and links (grey) correspond to species interactions. Variation in interaction frequencies are reflected by the width of the links. The network is arranged such that it shows minimal crossings of interactions, which allows for easier interpretation
