Fig. 3.
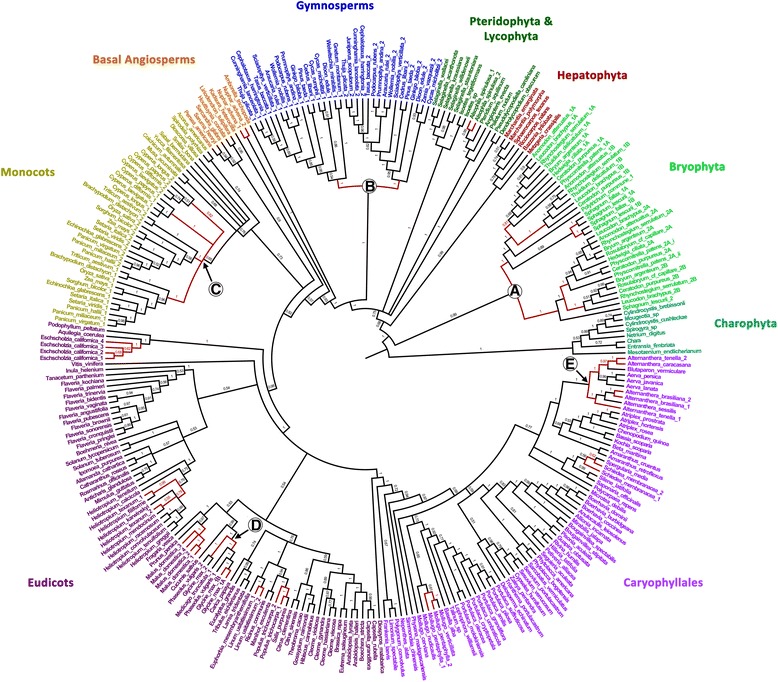
Bayesian gene tree showing the presence of transcripts encoded from RLSB homologs in land plants and Charophyte algae. Branch labels are posterior probabilities. Branches representing gene duplication or leading to duplicate copies are highlighted in red. Major events include: A, basal duplication in all Bryophytes, followed by subsequent duplication in Bryopsida and Sphagnum; B, basal duplication in all extant gymnosperms (although orthologs were not found in the RLSB2 gymnosperm clade for Gnetales); C, duplication in both the grass (Poaceae) and sedge (Cyperaceae) families (lack of support makes it unclear whether this represents duplication in each family or a single duplication event in a shared ancestor); D, duplication in Fabaceae; and numerous smaller-scale duplication events; E, the presence of two distinct and well-supported Alternanthera clades which are not sister to one another suggests duplication and loss within Amaranthaceae
