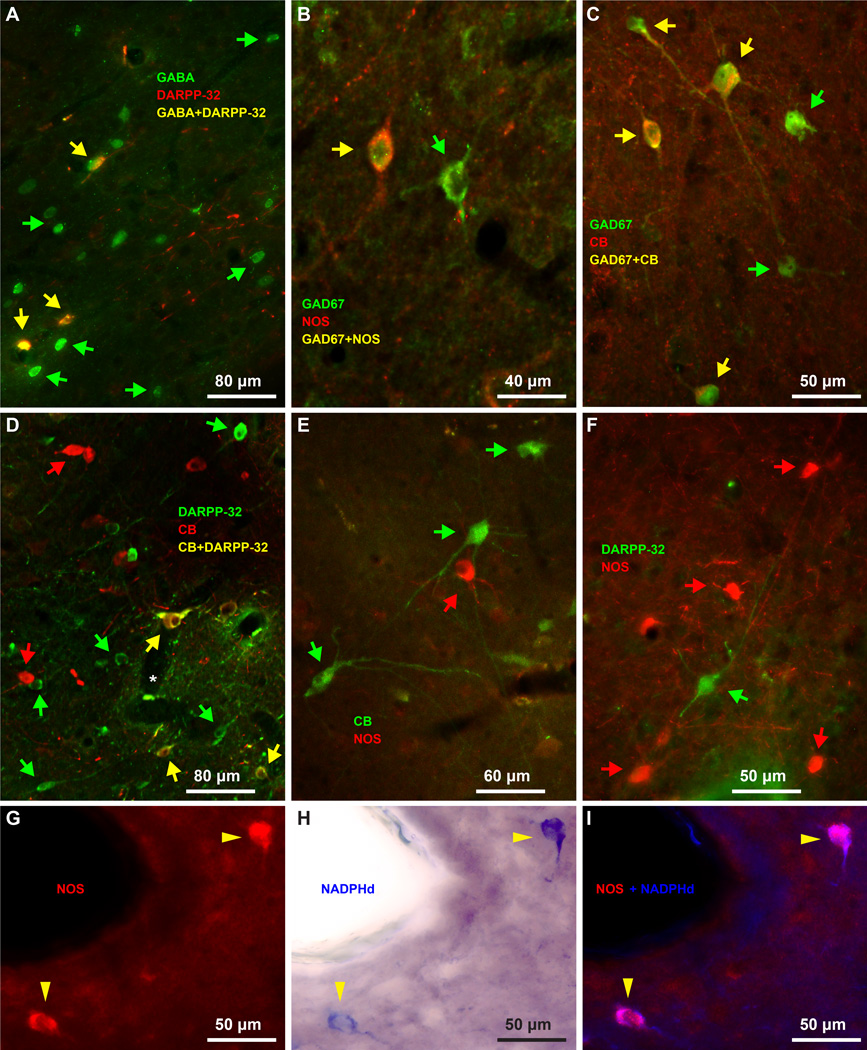
Figure 9.
Biochemical features of IM inhibitory neurons. A, All DARPP-32 neurons co-localize with GABA (yellow arrows). B–C, NOS neurons (B) and CB neurons (C) also express the inhibitory marker GAD67 (yellow arrows). D, Some IM neurons express DARPP-32 and calbindin (yellow arrows). E, CB expressing neurons (green arrows) do not overlap with NOS neurons (red arrows). F, DARPP-32 expressing neurons (green arrows) do not overlap with NOS neurons (red arrows). G–I, NOS and NADPHd co-localize in the same neurons (yellow arrowheads). The distinct neurochemical types of IM neurons are largely intermingled, however, in some cases (D, F) aspiny IM neurons appear to surround spiny IM neurons. Green and red arrows show some single-labeled neurons in panels A–F.