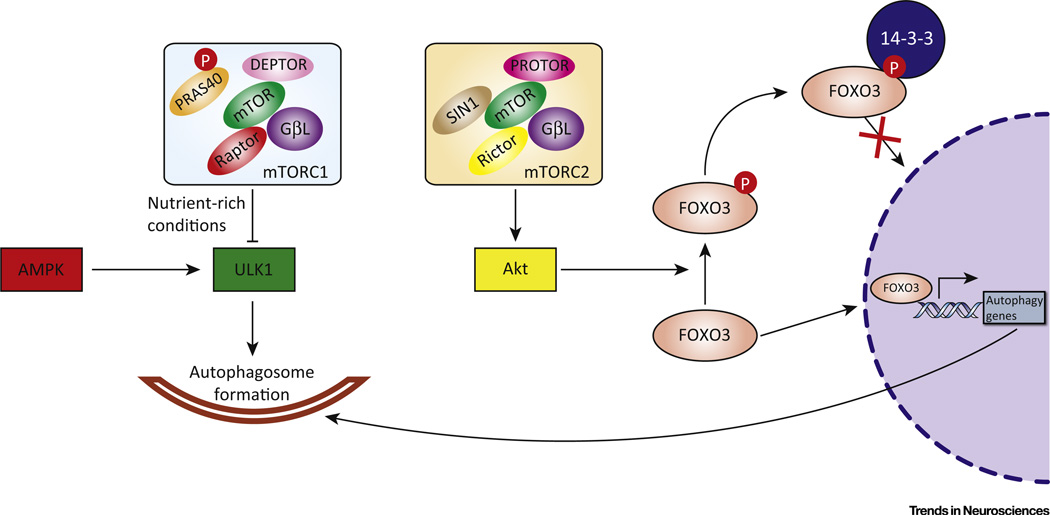
Figure 2. mTOR Regulatory Pathways of the Autophagy–Lysosomal Pathway (ALP).
mTORC1 is composed of mTOR, regulatory associated protein of mTOR (Raptor), G protein β-subunit-like protein (GβL), proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa (PRAS40), and DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein (Deptor). PRAS40 is phosphorylated (P) by Akt and dissociates from Raptor to activate mTORC1. Activated mTORC1 (in nutrient-rich conditions or in response to growth factors, etc.) phosphorylates ULK1 to inhibit its role in autophagosome formation. AMPK, however, phosphorylates ULK1 at different sites to activate autophagy. mTORC2 is composed of mTOR, rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR (Rictor), GβL, stress-activated protein kinase-interacting protein (SIN) 1, and protein observed with Rictor (PROTOR). mTORC2 can also participate in autophagy regulation through the FOXO3 pathway. mTORC2 phosphorylates Akt, followed by Akt phosphorylation of FOXO3. Phosphorylated FOXO3 binds to 14-3-3 protein, which retains it in the cytoplasm, preventing activation of autophagy gene transcription.