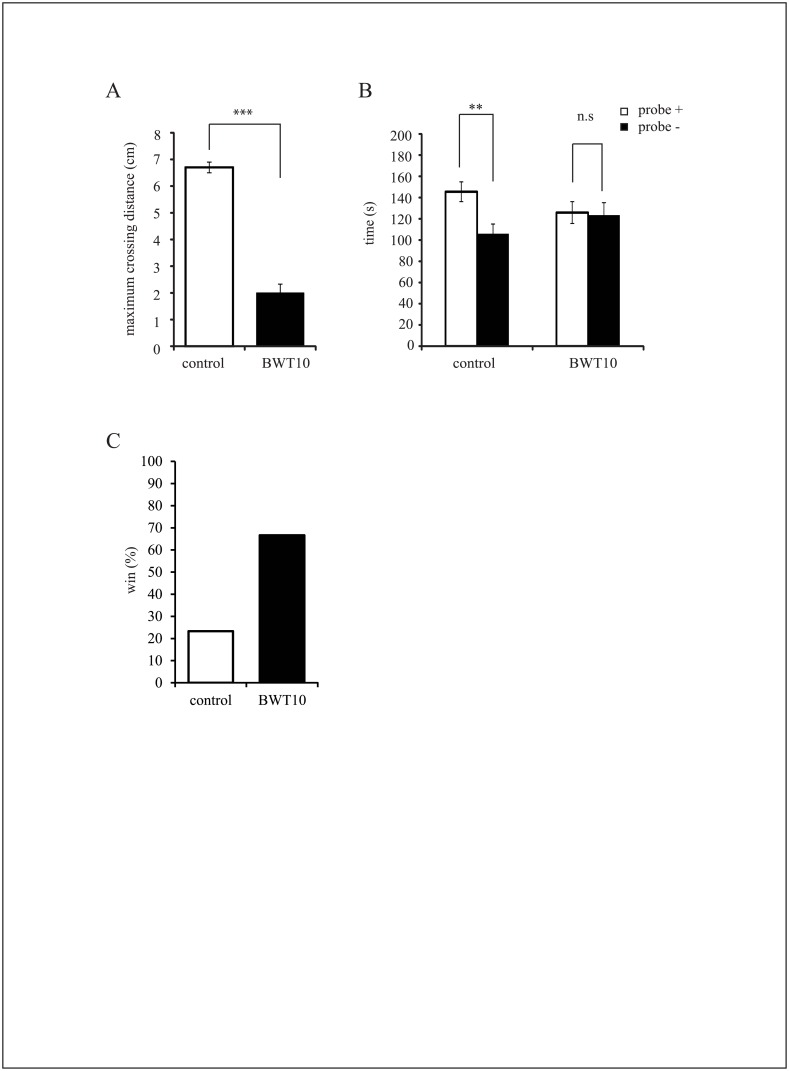
Fig 1. Neonatal whisker trimming disrupted tactile sensory performance and social interactions of mice in adulthood.
A, Adult BWT10 mice showed a significant deficit in gap-crossing performance compared to controls as evidenced by a shorter mean maximum crossable distance. Values are expressed as the mean ± SE. ***p < 0.001 versus control, Student’s t-test; n = 5 for control mice, and n = 6 for BWT10 mice. B, In the social interaction test, control mice showed a strong preference for the social side chamber containing a probe mouse, whereas adult BWT10 mice showed no such preference between the social and empty chambers. All values are expressed as the mean ± SE. **p < 0.01, n.s., no significance versus social chamber, Wilcoxon’s test; n = 23 for control mice, and n = 22 for BWT10 mice. C, In most trials, control mice retreated (“lost”) when BWT10 and control mice faced each other in the tube test apparatus. Values are expressed as the percentage of wins. *p < 0.05, significantly different from chance 50:50 outcome, χ test; n = 15 for control mice, and n = 15 for BWT10 mice.