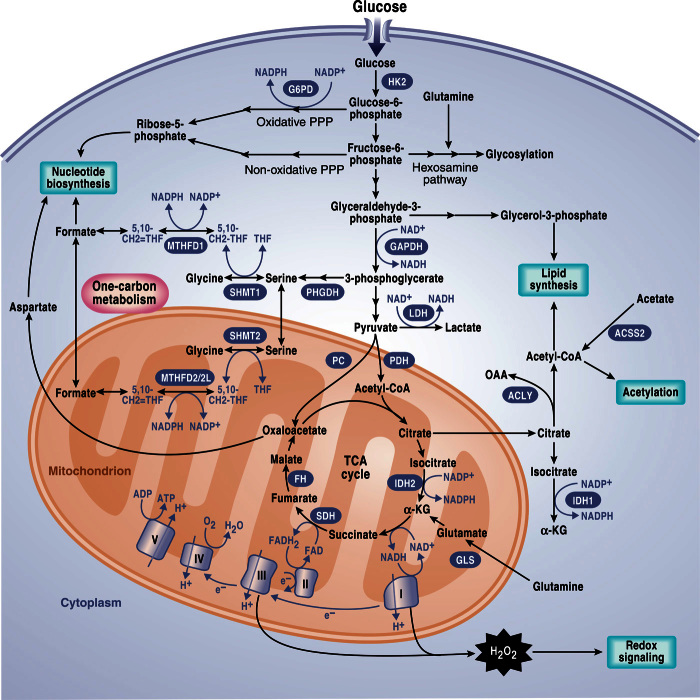
Fig. 3. Anabolic pathways that promote growth.
Glucose metabolism generates glycolytic intermediates that can supply subsidiary pathways including the hexosamine pathway, PPP, and one-carbon metabolism, all of which support cell growth. Mitochondrial TCA cycle intermediates such as oxaloacetate (OAA) and citrate are used to generate cytosolic aspartate and acetyl-CoA for nucleotide and lipid synthesis, respectively. Mitochondria also generate H2O2 and acetyl-CoA for redox signaling and acetylation, respectively. NADPH is used to drive anabolic reactions and to maintain antioxidant capacity. Cytosolic sources of NADPH include the oxidative PPP, IDH1, and enzymes from one-carbon metabolism including MTHFD1. Mitochondrial sources of NADPH include MTHFD2, MTHF2L, and IDH2. HK2, hexokinase 2; G6PDH, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; ACLY, ATP citrate lyase; GLS, glutaminase; SHMT, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; MTHFD2, methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2; MTHFD2L, MTHFD2-like; ACSS2, acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family member 2; THF, tetrahydrofolate.