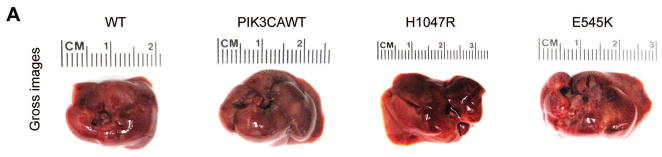
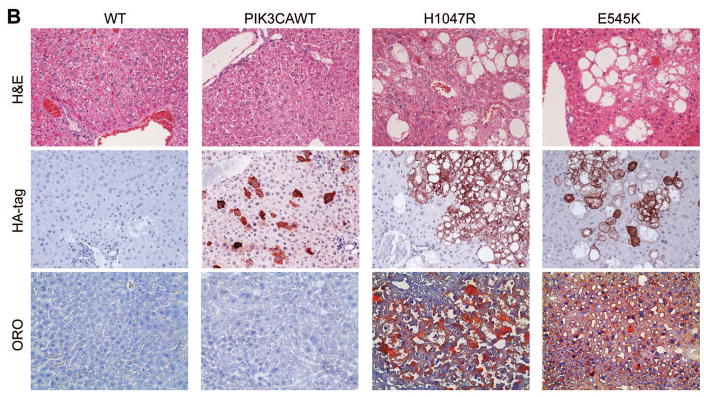
Fig. 1. Overexpression of PIK3CA H1047R and E545K mutants induces steatosis in the mouse liver.
(A) Gross images of livers from wild-type mice (WT), and mice injected with WT PIK3CA wild-type (PIK3CAWT), PIK3CA H1047R (H1047R), and PIK3CA E545K (E545K) constructs. PIK3CAWT, PIK3CA H1047R, and PIK3CA E545K mice were sacrificed 6 weeks post hydrodynamic injection. (B) Upper panels: hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of WT, PIK3CAWT, PIK3CA H1047R, and PIK3CA E545K mouse livers. While WT and PIK3CAWT livers were histologically undistinguishable from each other, PIK3CA H1047R and PIK3CA E545K livers displayed the presence of clusters of lipid-rich cells with an enlarged cytoplasm. Middle panels: the successful integration of PIK3CAWT, H1047R, and E545K genes was confirmed by strong immunoreactivity in hepatocytes for the HA-tag present in the transfected construct. Lower panels: Oil Red O (ORO) staining of WT, PIK3CAWT, PIK3CA H1047R, and PIK3CA E545K mouse livers showing intense staining only in PIK3CA H1047R and PIK3CA E545K livers. Magnifications: 200X.