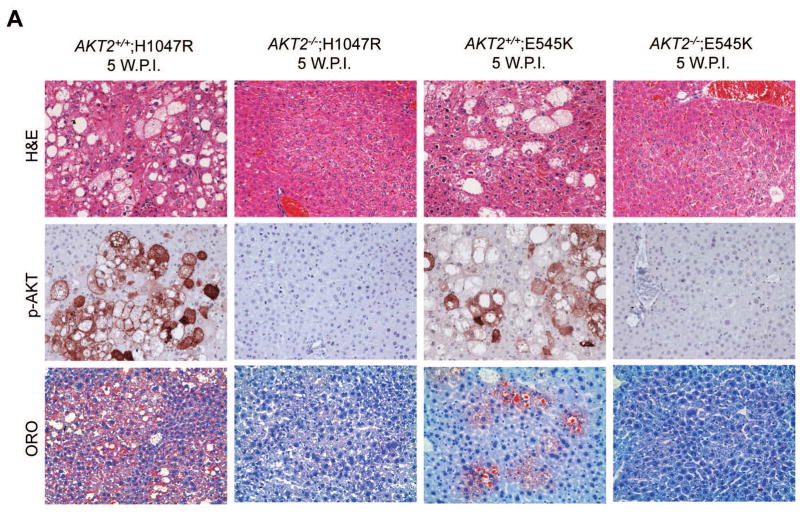
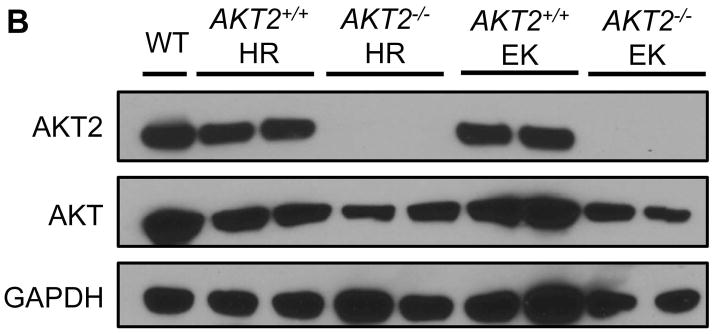
Fig. 4. Hepatic steatosis induced by overexpression of PIK3CA H1047R and E545K mutants requires AKT2.
(A) Upper panels: hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) of livers from AKT2 wild-type (AKT2+/+) or AKT2 knockout (AKT2−/−) mice injected with PIK3CA H1047R (H1047R) or PIK3CA E545K (E545K) constructs. While injection of the two PIK3CA mutants induced extensive liver steatosis in AKT2+/+ mice, the lipogenic phenotype driven by the two PIK3CA mutants was completely inhibited in AKT2−/− mice. Magnification: 200X. Middle panels: immunohistochemical staining of activated/phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) in the same mouse groups. Of note, p-AKT immunolabeling was completely abolished in AKT2−/− livers. Magnification: 200X. Lower panels: Oil Red O (ORO) staining in the same mouse groups confirming the findings of H&E-stained slides. Magnification: 200X. (B) Western blotting for AKT2 and AKT levels in livers from AKT2+/+ or AKT2−/− mice injected with PIK3CA H1047R (HR) or PIK3CA E545K (EK) constructs.