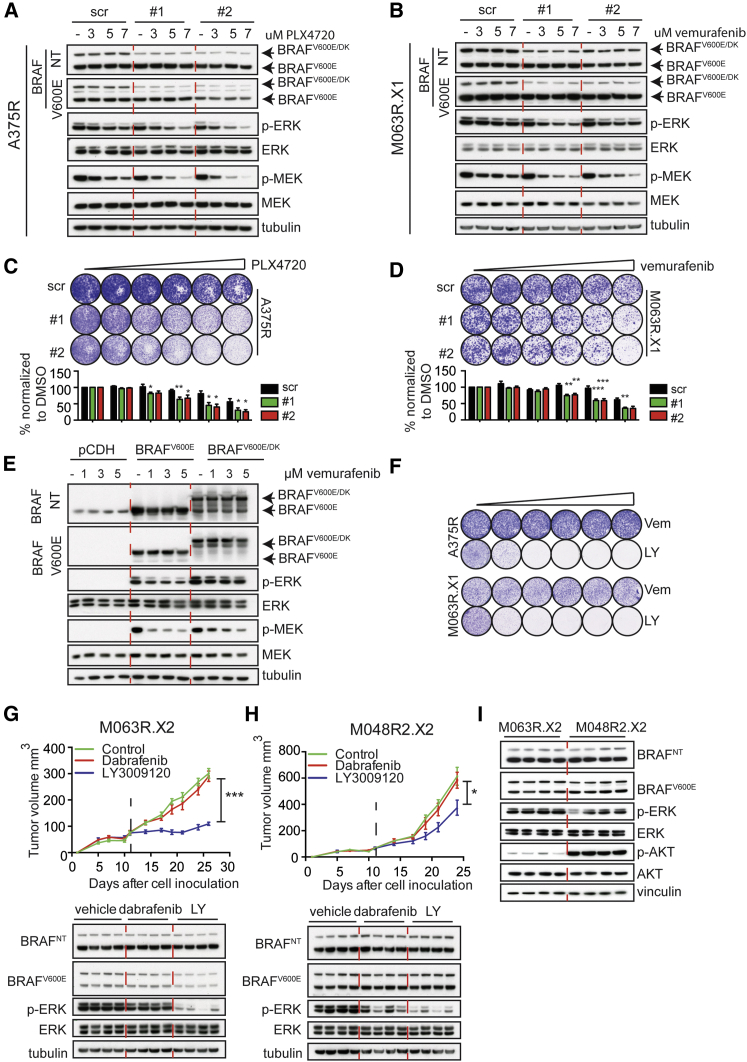
Figure 7.
BRAFV600E/DK Is Responsible for Resistance to BRAFi
(A and B) Immunoblotting of A375R (A) or M063R.X1 (B) cells infected with either scrambled shRNAs (scr) or two different shRNAs specifically targeting the BRAFV600E/DK. Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of inhibitor.
(C and D) Colony formation assays with A375R (C) or M063R.X1 (D) cells infected with either scrambled shRNAs (scr) or two different shRNAs specifically targeting the BRAFV600E/DK-encoding RNA (1 and 2). Cells were treated for 7 days with control vehicle or 1, 3, 5, 7, or 10 μM PLX4720 or vemurafenib. Graphs depict the normalization of six independent experiments. Unpaired t test was performed for each concentration of drug (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001). Error bars indicate SEM.
(E) Immunoblotting of HEK293T cells transfected with empty vector or a vector with BRAFV600E or BRAFV600E/DK, treated with vehicle or 1, 3, or 5 μM vemurafenib, is shown.
(F) Treatment of A375R and PDX-derived cell line M063R.X1 with increasing concentrations of vemurafenib (0.25−5 μM) or pan-RAF inhibitor LY3009120 (10 nM−1 μM) is shown.
(G and H) Treatment of two PDXs (M048R2.X2 and M063R.X2) that express the BRAFV600E/DK with 30 mg/kg dabrafenib or 15 mg/kg LY3009120 (n = 8 tumors/group). Graphs represent tumor volume and dashed lines indicate start of treatment. Unpaired t test was performed at the last time point (∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗∗p < 0.005). Error bars indicate SD. Lower part depicts the immunoblotting for p-ERK and BRAF on M048R2.X2 and M063R.X2, treated with either dabrafenib or LY3009120 (each lane represents a tumor derived from an individual mouse).
(I) Immunoblotting for basic levels (vehicle treated) of p-ERK and p-AKT in M063R.X2 and M048R2.X2 (each lane represents a tumor derived from an individual mouse) is shown.