Figure 7. Glycine currents deactivate faster for N46K compared to WT GlyRs .
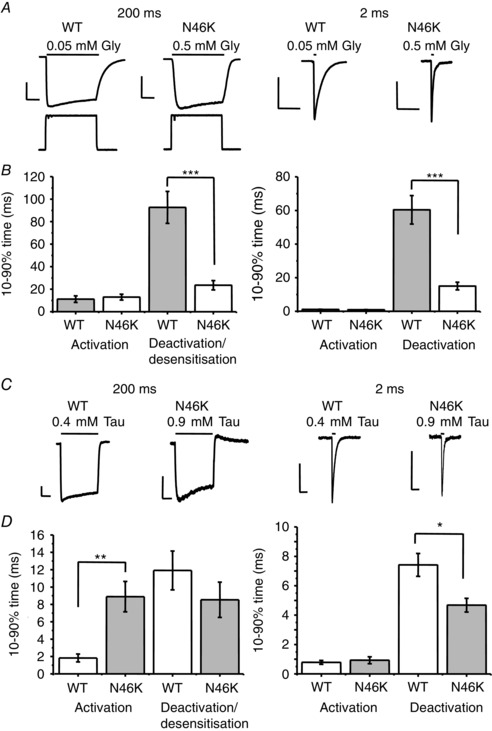
A, glycine currents recorded from outside‐out macropatches evoked by applying EC60 concentrations of glycine (Gly) for either 200 ms (left panel) or 2 ms (right panel) on HEK cells expressing WT GlyRs and N46K GlyRs. Open tip responses are shown in response to a pulse of 50% physiological salt solution/H2O. Calibration bars are 50 ms and 200 pA. B, bar graphs quantify the 10–90% glycine activation and deactivation/desensitisation rates (n = 6–9; ***P < 0.0001). C, recordings from outside‐out macropatches evoked by EC60 concentrations of taurine (Tau) for 200 ms (left panel) or 2 ms (right panel) on HEK cells expressing WT GlyRs (0.4 mm) and N46K GlyRs (0.9 mm). Calibration bars are 50 ms and 50 pA. D, bar graphs report the taurine 10–90% activation rates and also the deactivation/ desensitisation rates (n = 6–9; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005).
