Figure 2. Electrophysiological properties of T‐type currents in DRG neurons from WT and KI mice .
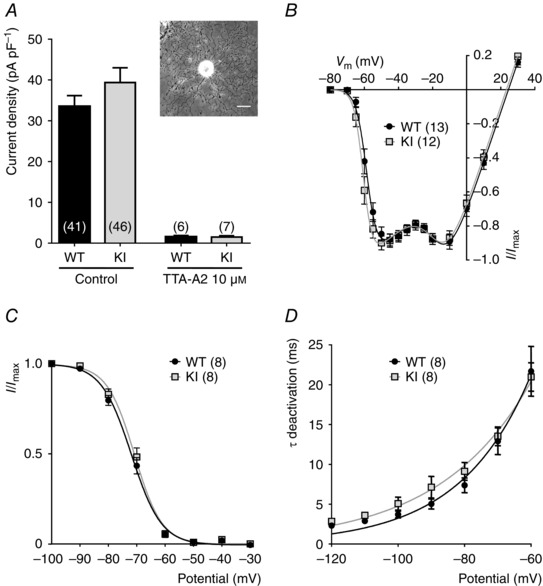
A, T‐type calcium current density in D‐hair DRG neurons from wild‐type (WT) and knock‐in (KI) mice, in control conditions (left) and in the presence of 10 μm of the T‐type channel inhibitor TTA‐A2 (right). For each cell, the current amplitude (in pA) was measured for a depolarization step from −80 to −30 mV and normalized for the cell capacitance (pF) in current density (pA pF–1). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Inset: bright field image of a typical D‐hair neuron with its ‘rosette’ morphology. Scale bar = 30 μm. B, normalized I–V relationship for the WT (grey square) and the KI (black circle) current evoked by 90 ms depolarizing step pulses from a holding potential at −80 mV. C, steady‐state inactivation curves obtained by stepping the membrane potential at −30 mV from conditioning depolarizing pulses ranging from −100 to −30 mV. D, deactivation kinetics as a function of the voltage.
