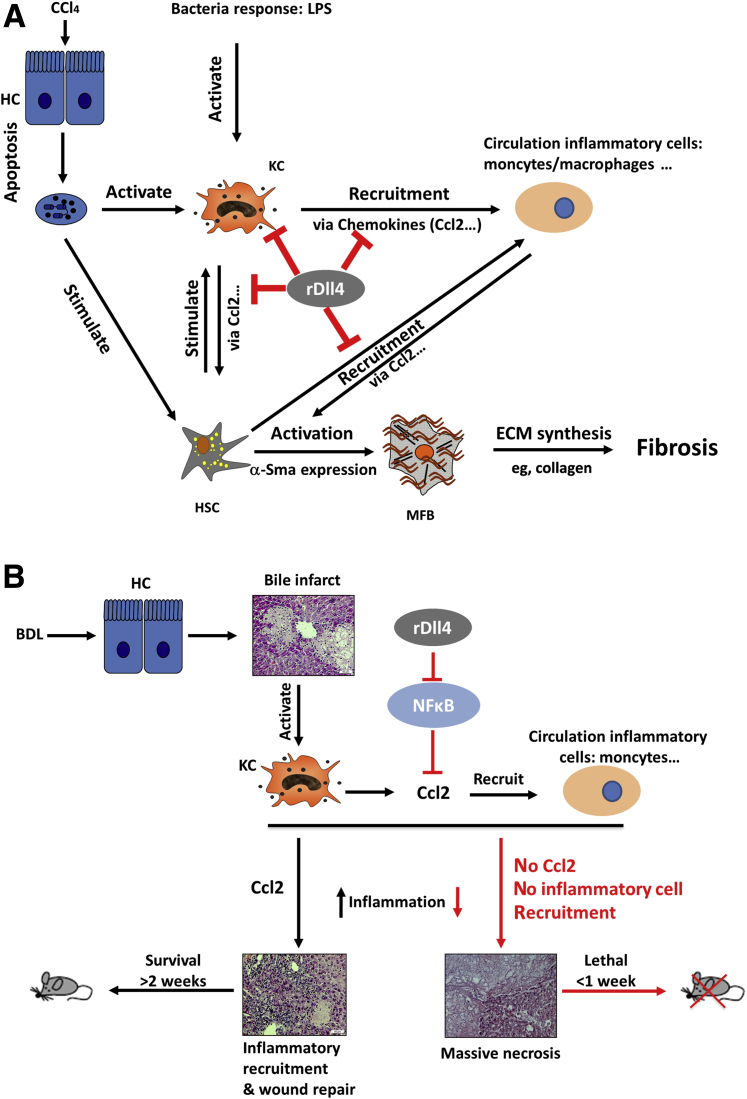
Figure 10.
Schemes summarizing the effects of recombinant Delta-like ligand 4 (rDll4) in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)- (A) and bile duct ligation (BDL)- (B) dependent liver damage. Three major aspects are associated with mechanisms of liver fibrogenesis: death of hepatocytes, inflammation, hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, and collagen synthesis. In the chronic CCl4-induced fibrotic models, rDll4 comprehensively inhibited each of these. However, in vitro experiments clearly show that rDll4 has no direct effect on hepatocyte apoptosis, HSC activation, and collagen production. rDll4 remarkably inhibits chemokines, particularly chemokine ligand (Ccl)2, both in vivo and in vitro. In the bile duct ligation (BDL) model, rDll4 application has a fatal effect, visualized by the survival curves, through inhibition of Ccl2. The BDL mice receiving rDll4 are rescued when they are subjected to rCcl2 application. Thus, rDll4 improves liver fibrosis in chronic CCl4 models via inhibition of chemokines. HC, hepatocyte; HSC, hepatic stellate cells; KC, Kupffer cell; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MFB, myofibroblasts.