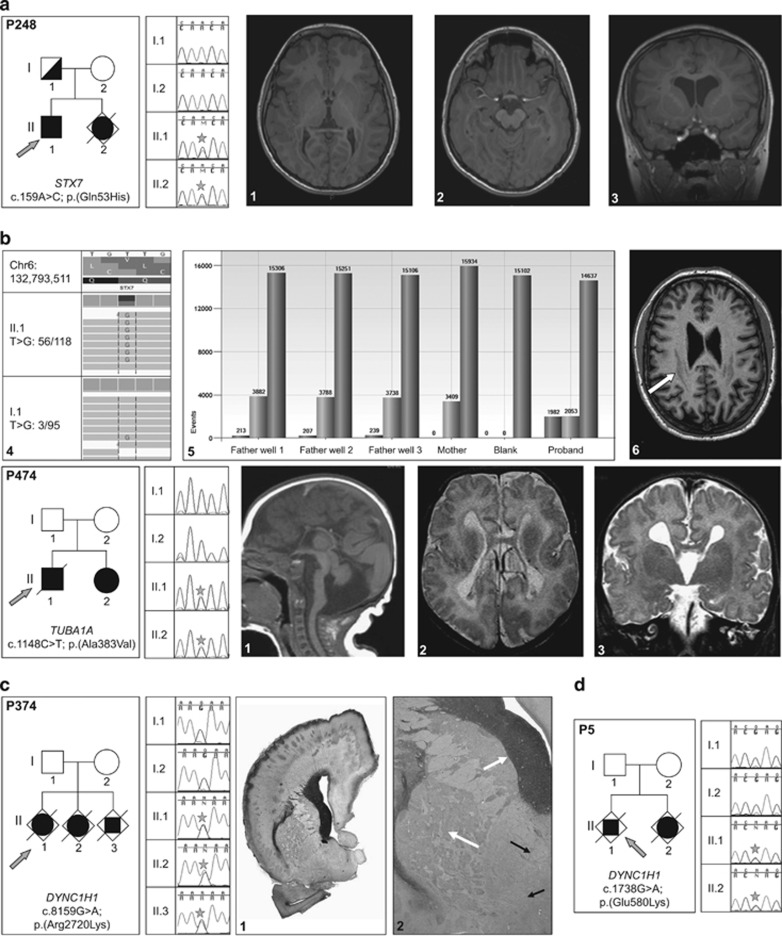
Figure 1.
Families with parental germline mosaic variants. (a) P248-STX7 variant. (a1, a2, a3) Proband's MRI sections showing the extended heterotopic band. (a4) WES reads showing the STX7 variant and one variant read in the father. (a5) Droplet digital PCR data confirming the somatic mosaicism in the father: variant allele is present in 213 out of 3882 positive droplets in first father well; 207 out of 3788 in second well; 239 out of 3738 in third well; absent in the mother and present in 1982 out of 2053 droplets in the proband. (a6) Father's MRI showing the milder posterior band heterotopia (arrow). (b) P474-TUBA1A variant. (b1, b2, b3) Patient's MRI sections showing the corpus callosum agenesis, brainstem and cerebellum abnormalities, bilateral opercular dysplasia and dysmorphic ventricular horns. (c) P374-DYNC1H1 mutation. (c1, c2) Histopathological sections showing heterotopic neuronal cells, extended polymicrogyria, enlarged germinative zones and disorganized axonal tracts (arrows). (d) P5-DYNC1H1 variant. Star symbol is to highlight position of heterozygous mutation in affected individuals.