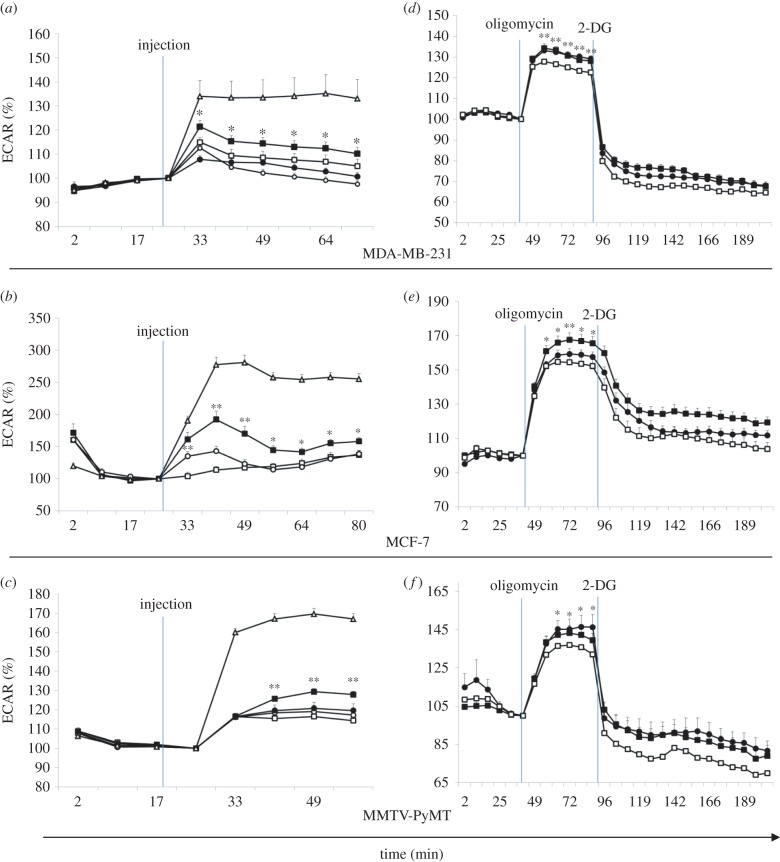
Figure 4.
CCL5 increases rate of glycolysis and cellular glycolytic capacity. A Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analyzer was used to detect real-time changes in extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) as measurements of the rate of glycolysis. (a–c) The indicated compounds were injected at the indicated time. Percentage changes in ECAR were measured, □, medium; ▪, CCL5; ○, CCL5 + maraviroc; •, CCL5 + rapamycin; Δ, oligomycin. (d–f) Glycolytic stress test. Cells were untreated (medium alone) or treated with 10 nM CCL5 for 3 or 23 h. As indicated 2 µM oligomycin was introduced followed by the glycolysis inhibitor 2-DG, at the indicated times. Percentage change in ECAR was measured. □, medium; ▪, 10 nM CCL5, 3 h; •, 10 nM CCL5, 23 h. Values are the means ± s.e. of three combined independent experiments, with all treatments being performed as 12 replicates. Statistical analysis was performed comparing no treatment with CCL5 treatment: *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.