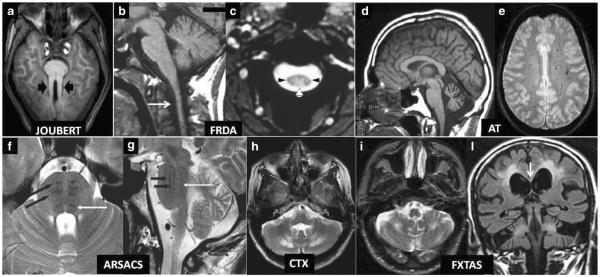
Fig. 2.
a–l Diagnostic biomarkers of recessive and X-linked inherited ataxias on conventional MRI. Axial T1 weighted image (a) showing symmetrically thickened and parallel oriented superior cerebellar peduncles (black arrowheads) creating the “Molar Tooth” sign characteristic of Joubert syndrome and related disorders. Note also the small and dysmorphic vermis. Sagittal T1-weighted image (b) shows atrophy of the medulla and cervical spinal cord (arrow) in a case of Friedreich ataxia (FRDA). Axial T2*-weighted gradient echo image (c) confirms the decreased size of the cervical cord cross-section in the same disease and demonstrates symmetric hyperintensity of the posterior (white arrowhead) and lateral (black arrowheads) columns of the spinal cord (both images reprinted with permission from ref. [1]). Sagittal T1-weighted image (d) demonstrates widened vermian sulci in a patient with ataxia telangectasia (AT) consistent with a macroscopic pattern of cerebellar cortical atrophy (image reprinted with permission from ref. [1]). Axial T2*-weighted gradient echo image (e) demonstrates multiple hypointense dots in the centrum semiovalis WM consistent with capillary telangectasias in another patient with AT (image reprinted with permission from ref. [128]). Axial (f) and sagittal (g) T2-weighted images in a patient with recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSA CS) show characteristic low signal intensity stripes (black arrows) corresponding to the corticospinal tracts in a bulky basis pontis. The white arrow in f and g indicates the hypointense medial lemniscus (both images reprinted with permission from ref. 129). Axial T2-weighted image (h) shows characteristic symmetric hyperintensity of the peridentate cerebellar WM in a patient with cerebroendineous xanthomatosis (image reprinted with permission from [130]). Axial T2-weighted image (i) in a patient with Fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) shows symmetric hyperintensity of the cerebellar WM which is accompanied in a coronal T2-weighted FLAIR image (l) by symmetric extensive areas of hyperintensity of the cerebral WM and of the splenium of the corpus callosum (arrow). Joubert Joubert syndrome and related disorders; FRDA Friedreich's ataxia; AT ataxia telangectasia; ARSACS autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay; CTX cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis; FXTAS Fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome