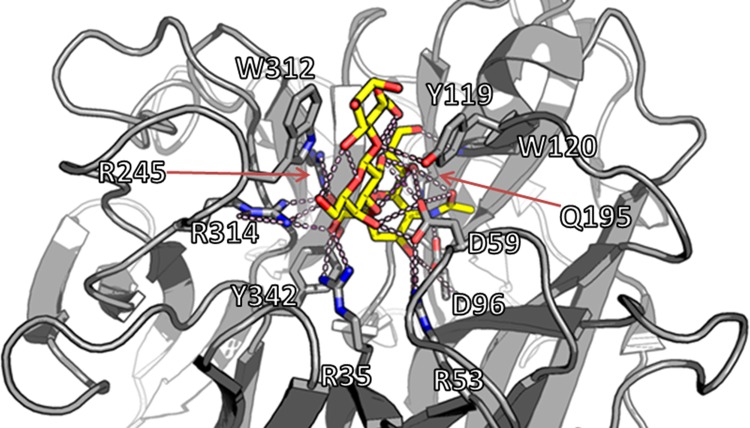
Fig 1. The active site of the trans-sialidase from Trypanosoma cruzi (TcTS).
The 3’-sialyllactose substrate (yellow) is shown positioned in the active site of TcTS. The active site residues (top 9 residues in Table 1) bind the sialic acid moiety of the substrate by a number of hydrogen bonds (A), whereas the aromatic sandwich (W312 and Y119) aligns to the lactose moiety and binds it in the tight cleft above the active site (B). An overview of the interactions between enzyme and substrate is given in Table 1. The model is based on PDB entry 1S0I [11].