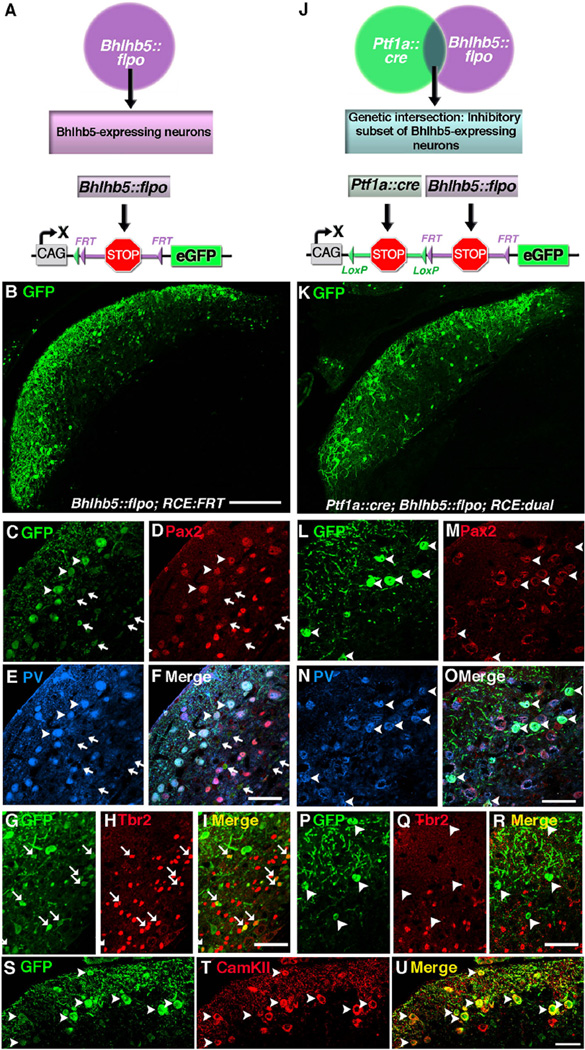
Fig. 4.
Dual intersectional strategy distinguishes subpopulations of Bhlhb5-expressing cells: cartwheel and unipolar brush neurons. (A) Schematic illustrating the use of the Bhlhb5::flpo with RCE::FRT to label Bhlhb5-expressing neurons. (B–I) Coronal sections of the DCN from an adult Bhlhb5::flpo; RCE::FRT mouse immunostained with antibodies against GFP, Pax2, parvalbumin (PV), or Tbr2, as indicated. (J) Schematic illustrating the use of Bhlhb5::flpo, Ptf1a::cre and RCE::dual to label a population of neurons at the genetic intersection, namely the inhibitory subset of Bhlhb5-expressing neurons. (L–R) Coronal sections of the DCN from an adult Ptf1a::cre; Bhlhb5::flpo; RCE::dual mouse immunostained with antibodies against GFP, Pax2, parvalbumin (PV), or Tbr2, as indicated. (S–U) Coronal sections of the DCN from an adult Bhlhb5::flpo; RCE::FRT mouse immunostained with antibodies against GFP, CamKIIα, as indicated. Images are single confocal optical plane of coronal sections from six- to eight-week old mice. Arrowheads and arrows indicate examples of double-labeled inhibitory and excitatory neurons, respectively. Scale bars: B, K = 200 µm; all others = 50 µm.