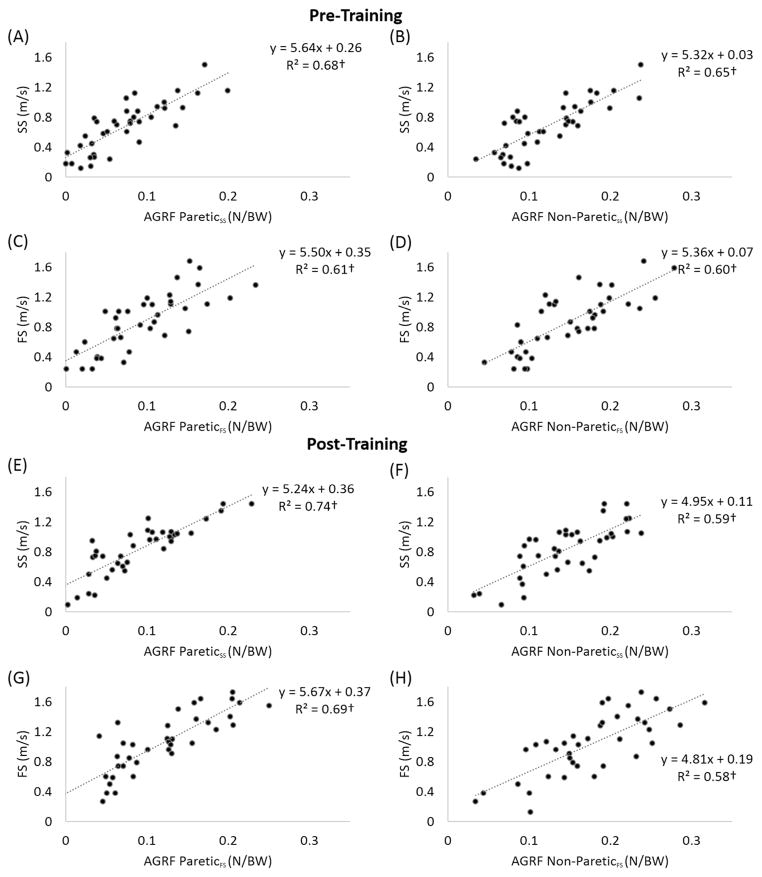
Figure 2.
Relationships between anterior ground reaction force (AGRF) and walking speed (N=38). (A–D): Pre-training. (E–H): Post-training. “SS” denotes self-selected walking speed and “FS” denotes faster walking speed. “BW” denotes the bodyweight. “†” indicates p < 0.01. (A) Relationship between paretic propulsive force and self-selected walking speed at pre-training. (B) Relationship between non-paretic propulsive force and self-selected walking speed at pre-training. (C) Relationship between paretic propulsive force and faster walking speed at pre-training. (D) Relationship between non-paretic propulsive force and faster walking speed at pre-training. (E) Relationship between paretic propulsive force and self-selected walking speed at post-training. (F) Relationship between non-paretic propulsive force and self-selected walking speed at post-training. (G) Relationship between paretic propulsive force and faster walking speed at post-training. (H) Relationship between non-paretic propulsive force and faster walking speed at post-training.