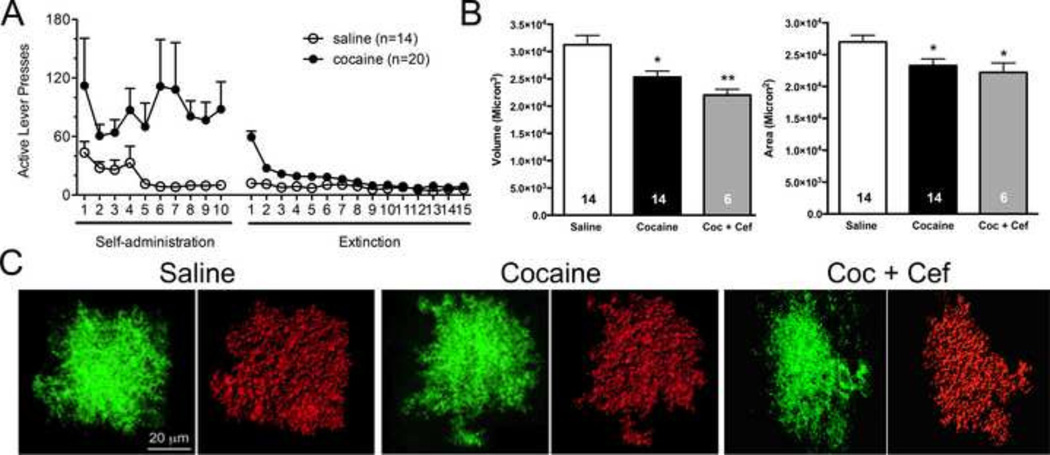
Figure 3. 3D reconstruction of individual NAcore astrocytes following cocaine or saline experience.
A) Animals were trained to self-administer cocaine or saline, and were then taken through extinction training. A subset of cocaine-administering rats received either saline or vehicle during extinction training. B) Following rodent behavioral procedures, astrocyte GFP signals from AAV5 GFAP-Lck-GFP transduced cells were used to generate 3D space filling models. Following deconvolution of Z-series datasets, 3D volumes generated by IMARIS were constructed, which recapitulated the shape and contours of astroglial cells transduced with the membrane localized GFP. Space filling models were then used to determine surface area (microns2) and volume (microns3) of NAc core astrocytes following cocaine or saline exposure. C) Cocaine exposure significantly reduced astroglial volume as determined by analysis of IMARIS space filling astrocyte models (shown above in figure 2). Two-tailed t-tests revealed a significant reduction following cocaine exposure. Cocaine exposure also significantly reduced astroglial surface area, * p<0.05, **p<0.01.