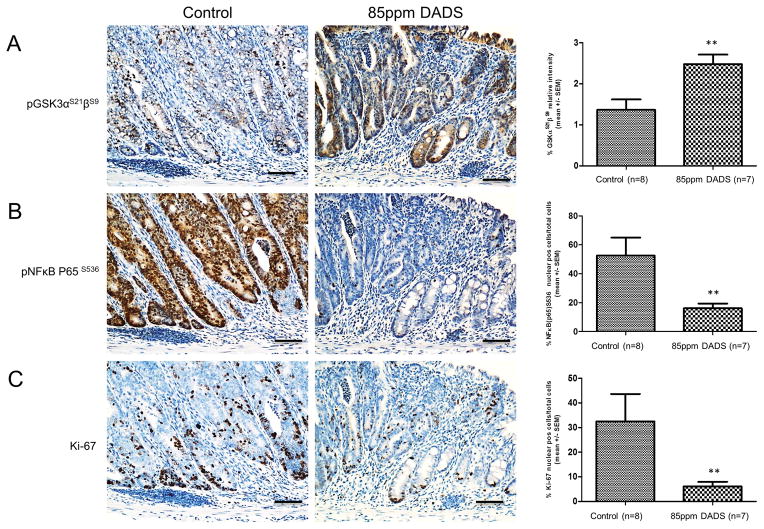
Figure 5.
Diallyl disulfide (DADS) induced GSK-3α/β phosphorylation at S21/9, inhibited nuclear localization NFkB (P65) phosphylated at S536, and Ki-67 expression in vivo. A–C, IHC analysis p-S21/9 GSK-3α/β (1:100), p-S536-NFκB (P65) (1:100), and Ki-67 (1:100) in colonic epithelium at day 52 from mice from AOM/DSS control group or 85ppm DADS group. A, DADS induced inhibition of GSK-3α/β as shown by increased phosphorylation at S21/9 with both cytoplasmic and nuclear localization. B, DADS reduced expression of p-S536-NFκB (P65) in nucleus. C, DADS inhibited proliferation as shown by staining with Ki-67. Scale bar= 100μm. Right panels are quantitation of staining using Aperio Scanscope nuclear staining program. **P < 0.01 indicates a significant difference compared with control group as determined by t-test.