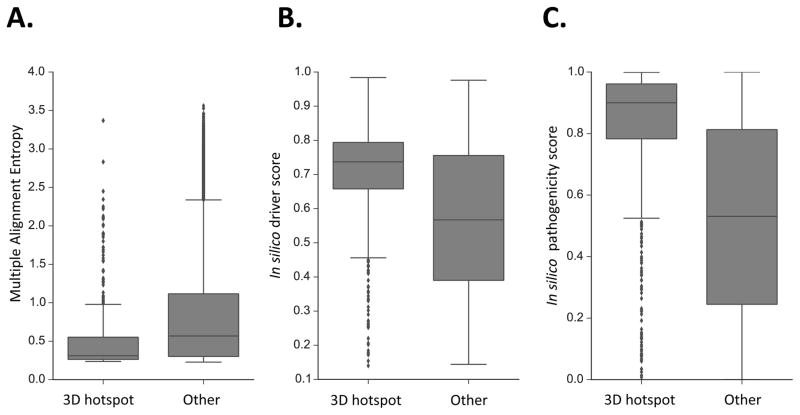
Fig. 1. 3D Hotspot regions are different from other mutated protein residues.
Three distinguishing features of HotMAPS regions. A. HotMAPS mutated residues are more conserved in vertebrate evolution than mutated residues not in hotspot regions, as shown by lower Multiple Alignment Entropy (p=1.2E-29; Mann-Whitney U test). Multiple Alignment Entropy is calculated as the Shannon entropy of protein-translated 46-way vertebrate genome alignments from UCSC Genome Browser, which is lowest for the most conserved residues. B. HotMAPS missense mutations have higher in silico cancer driver scores from the CHASM algorithm (p=5.3E-47; Mann-Whitney U test) than those mutations not in hotspot regions, and C. higher in silico pathogenicity scores from the VEST algorithm (p=7.0E-162; Mann-Whitney U-test). Finally, HotMAPS mutated residues occur more frequently at protein-protein interfaces (p=1.3E-11; one-tailed Fisher’s Exact test) (Table S8).