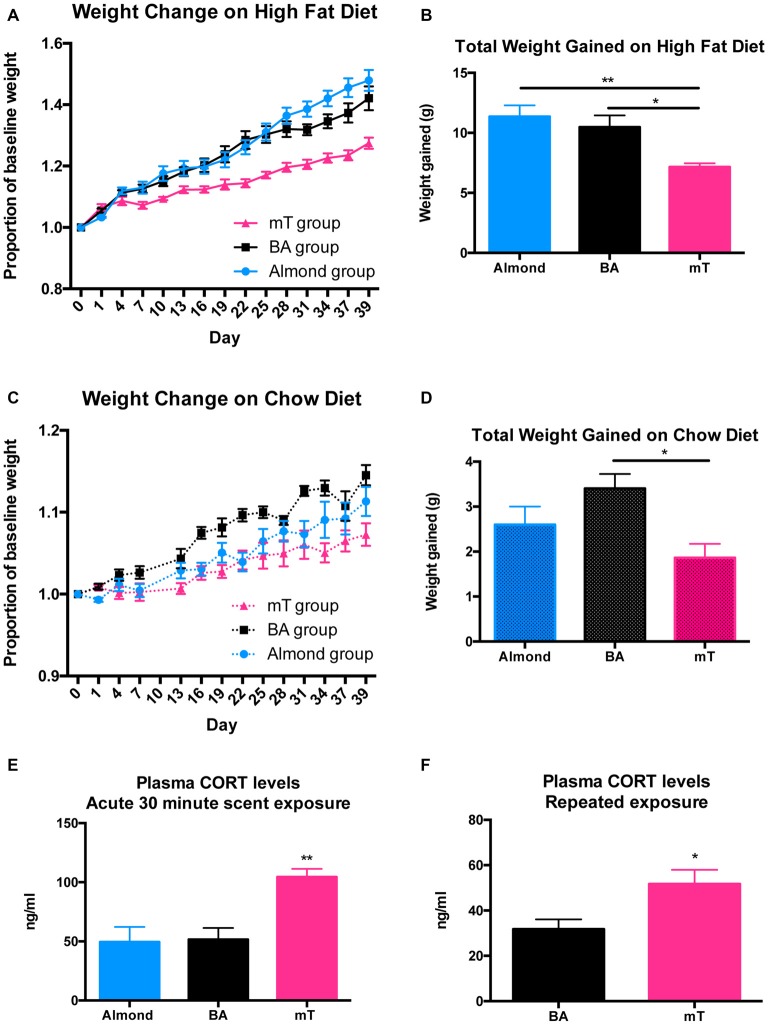
Figure 2.
Chronic mT exposure attenuates weight gain in both low and high fat diets (HFDs). Six cages of group housed (n = 5 per cage) were exposed daily to 9.8 μl mT, 52.8 μl BA, or 30 μl almond scent for 6 weeks while on a chow (5% fat) or high fat (45% fat, HFD) diet. (A) Weight gain on HFD presented as fold change from baseline weight. (B) Total weight gained on HFD at the end of the 6-week experiment. mT-exposed mice gained significantly less weight than BA or Almond exposed groups. (C) Weight gain on chow diet presented as fold change from baseline weight. (D) Total weight gained on chow diet. mT-exposed mice gained significantly less weight than BA-exposed mice on a chow diet. (E) Plasma corticosterone (CORT) levels from trunk blood after a single 30-min exposure to 9.8 μl mT, 52.8 μl BA, or 30 μl almond scent. (F) Plasma CORT levels from trunk blood after 3 weeks of daily scent exposure (and immediately after the final 30 min scent exposure). All error bars shown represent SEM.