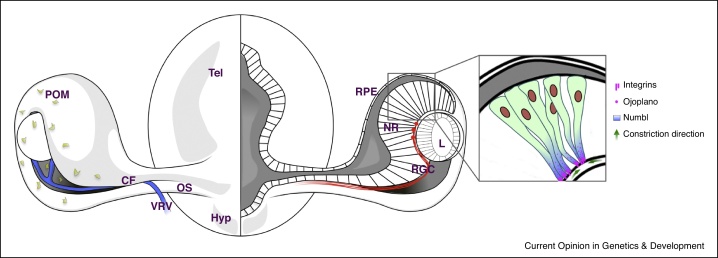
Figure 3.
Generation of the choroid fissure during optic cup formation. Schematic frontal view of the forebrain showing the eyes and (inset) polarized retinal neuroepithelial cells during optic cup morphogenesis. The left side of the main figure shows a surface view of the optic vesicle and ventrally positioned choroid fissure. POM cells (green) surround the optic cup, invade the choroid fissure and later form the blood vessels of the eye (blue). The right side of the main figure shows a slice through the optic cup at the level of the choroid fissure. Retinal ganglion cell axons (red) use the fissure as a route out of the eye as they navigate towards central targets in the brain. The inset shows a higher resolution view of neuroepithelial cells in the neural retina. The basal end feet of these cells localize Integrin in an Ojoplano and Numb/Numbl dependent mechanism, and their constriction (green arrows) is thought to contribute to neuroepithelial bending and the invagination process. Based largely on Martinez-Morales et al. [48] and Bogdanović et al. [49•]. Abbreviations: CF, choroid fissure; Hyp, hypothalamus; L, Lens; NR, neural retina; OS, optic stalk; POM, periocular mesenchyme; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; RGC, retinal ganglion cells; Tel, telencephalon; VRV ventral retinal blood vessels.