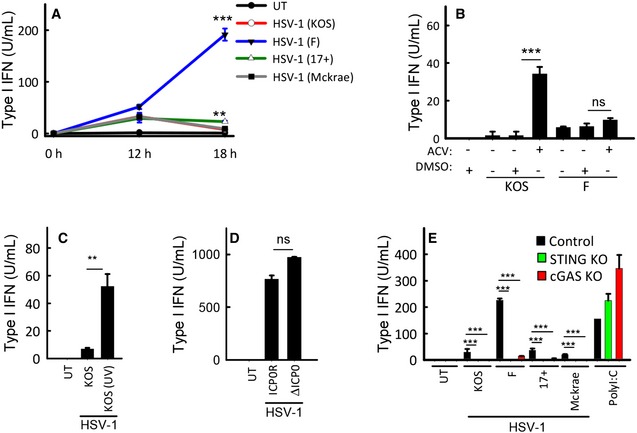
THP1 cells were infected with the shown strains of HSV‐1 (MOI 3). Supernatants were harvested from untreated cultures or cells infected for 12 or 18 h for measurement of type I IFN bioactivity.
THP1 cells were treated with 0.1 μg/ml of acyclovir (ACV) and infected with the KOS and F HSV‐1 strains (MOI 3). Supernatants were harvested 18 hpi for measurement of type I IFN bioactivity.
THP1 cells were treated with infectious or UV‐inactivated HSV‐1 (strain KOS). Supernatants were harvested 18 hpi for measurement of type I IFN bioactivity.
MDMs were infected with ICP0‐deficient or revertant HSV‐1 (strain KOS, MOI 3). Supernatants were harvested 18 hpi for measurement of type I IFN bioactivity.
THP1‐derived cells deficient for cGAS or STING were infected with the shown strains of HSV‐1 (MOI 3) or stimulated with poly(I:C) (2 μg/ml). Supernatants were harvested 18 hpi for measurement of type I IFN bioactivity.
Data information: Data are presented as means of triplicates ± SD; symbols for
P‐values: **0.001 <
P < 0.01; ***
P < 0.001; ns, not significant.