-
A, B
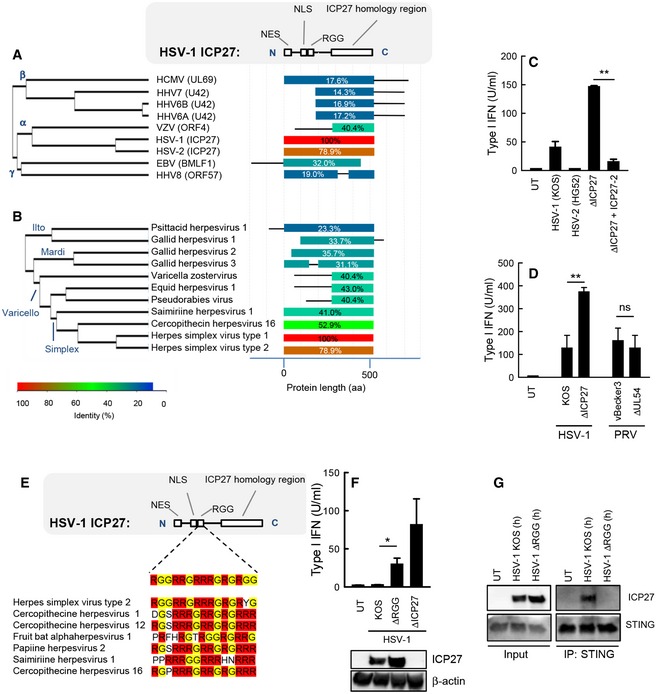
Alignment of the ICP27 homologs of the human herpesviruses (A) and a series of alpha‐herpesviruses (B). The diagram to the right illustrates the degree of similarity with HSV‐1 ICP27 and the distribution within the molecules.
-
C
THP1 cells were infected with HSV‐1 (KOS), HSV‐2 (HG52), HSV‐1 ΔICP27, or HSV‐1 ΔICP27 rescued with HSV‐2 ICP27 (MOI 3). Supernatants were harvested 18 hpi for measurement of type I IFN bioactivity.
-
D
RAW264.7 cells were infected with HSV‐1 (KOS), PRV (vBecker3) and the corresponding mutants lacking ICP27 (UL54 in the case of PRV). Supernatants were harvested 18 hpi for measurement of type I IFN bioactivity.
-
E
Alignment of the RGG box of in ICP27 proteins of the simplex virus genera of alpha‐herpesviruses.
-
F
THP1 cells were infected with HSV‐1 (KOS), ΔRGG, or ΔICP27 (MOI 3). Supernatants were harvested 18 hpi for measurement of type I IFN bioactivity. ICP27 expression in the infected cells was determined by Western blotting.
-
G
THP1 cells were infected with HSV‐1 KOS or HSV‐1 ΔRGG (MOI 10) for 8 h, and total lysates were generated. STING was immunoprecipitated and subjected to Western blotting using antibodies against ICP27 and STING.
Data information: Data in (C, D, and F) are presented as means of triplicates ± SD; symbols for
P‐values: *0.01 <
P < 0.05; **0.001 <
P < 0.01; ns, not significant.
Source data are available online for this figure.