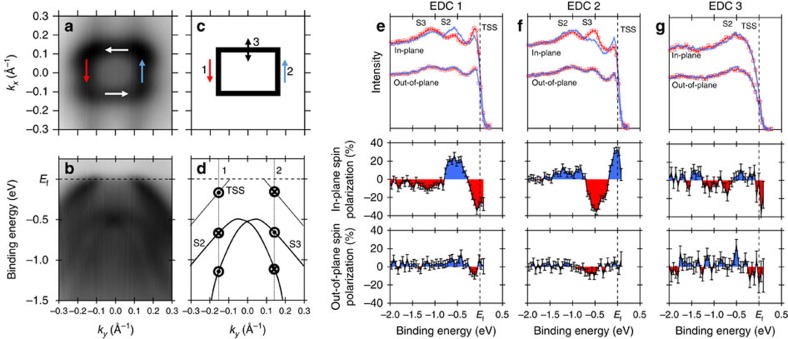
Figure 5. Spin texture of the topologically non-trivial surface state.
(a) Constant binding energy surface with a photon energy of 16 eV highlighting the surface state with linear dispersion. (b) In-plane ARPES dispersion along the 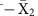 direction emphasizing the position of the surface state with linear dispersion and the lower Rashba-like surface state. (c) Schematic FS diagram depicting the location of energy distribution curves (EDCs) 1–3. (d) Schematic in-plane ARPES dispersion with the measured in-plane spin-polarization marked. The surface state with linear dispersion shows strongly opposing polarizations on either side. Furthermore, the spin polarization for Rashba-like surface state alternates as expected. (e–g) EDCs and spin polarizations for the noted locations. Measured intensities are shown for the in-plane and out-of-plane spin EDCs. For in-plane spin polarization, positive (blue) spin polarizations correspond to polarization towards positive kx, negative (red) spin polarizations correspond to polarization towards negative kx. For out-of-plane spin polarization, positive (blue) spin polarizations correspond to polarization towards positive kz, negative (red) spin polarizations correspond to polarization towards negative kz. Consequently, considering EDCs 1–3 we note the presence of a anticlockwise helical spin texture with minimal radial component. Error bars are correspond to the statistical error from counting statistics (further discussion in Supplementary Note 4).
direction emphasizing the position of the surface state with linear dispersion and the lower Rashba-like surface state. (c) Schematic FS diagram depicting the location of energy distribution curves (EDCs) 1–3. (d) Schematic in-plane ARPES dispersion with the measured in-plane spin-polarization marked. The surface state with linear dispersion shows strongly opposing polarizations on either side. Furthermore, the spin polarization for Rashba-like surface state alternates as expected. (e–g) EDCs and spin polarizations for the noted locations. Measured intensities are shown for the in-plane and out-of-plane spin EDCs. For in-plane spin polarization, positive (blue) spin polarizations correspond to polarization towards positive kx, negative (red) spin polarizations correspond to polarization towards negative kx. For out-of-plane spin polarization, positive (blue) spin polarizations correspond to polarization towards positive kz, negative (red) spin polarizations correspond to polarization towards negative kz. Consequently, considering EDCs 1–3 we note the presence of a anticlockwise helical spin texture with minimal radial component. Error bars are correspond to the statistical error from counting statistics (further discussion in Supplementary Note 4).