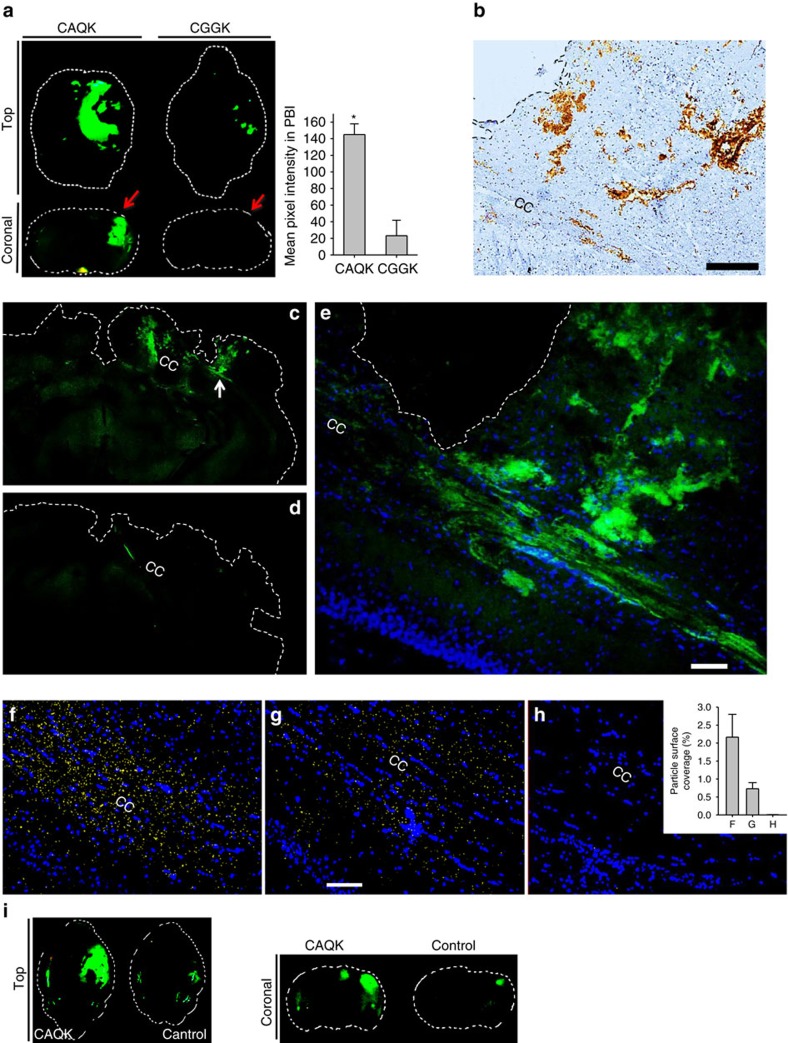
Figure 2. CAQK peptide shows selective homing to PBI.
(a) Fluorescence brain images (top view and coronal view) of mice injected with FAM-labelled peptides 6 h after PBI. Animals were perfused, brains isolated and imaged under an Illumatool System (green channel). (*P<0.05, ANOVA analysis, n=6); mean±s.e.m. (b) FAM-CAQK in the sections from injured brain was visualized by immunohistochemical staining for FAM (brown) from FAM-CAQK in PBI. Sections counterstained with haematoxylin brains isolated (blue). Scale bar, 100 μm. (c–e) Fluorescence signal of FAM-CAQK (C) and FAM-Control (D) in clarified PBI brains. Peptides injected 6 h after PBI were allowed to circulate for 30 min followed by the CLARITY protocol for clearing brains. (e) shows higher magnification from c (white arrow points to the magnified region). CAQK showed homing to fibre-like structures in the corpus callosum (CC) area. Scale bar, 50 μm. (f–h) CAQK conjugated AgNPs bind to PBI sections around the CC. Overlay experiments using peptide-conjugated AgNPs on frozen PBI sections counterstained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue), green AgNPs were pseudo coloured to yellow for higher colour contrast, and the threshold was equally enhanced for all samples using Image J. Shown are representative sections of CAQK-NP binding to PBI sections (f), CAQK-NP binding to healthy brain sections (g) and control-NP binding to PBI sections (h). The number of particles in three fields were counted and plotted in the bar diagram from three brains. Scale bar, 50 μm. Mean±s.e.m. (i) Fluorescence brain images (top view and coronal view) of mice injected with FAM-labelled peptides 6 h after a controlled cortical injury.