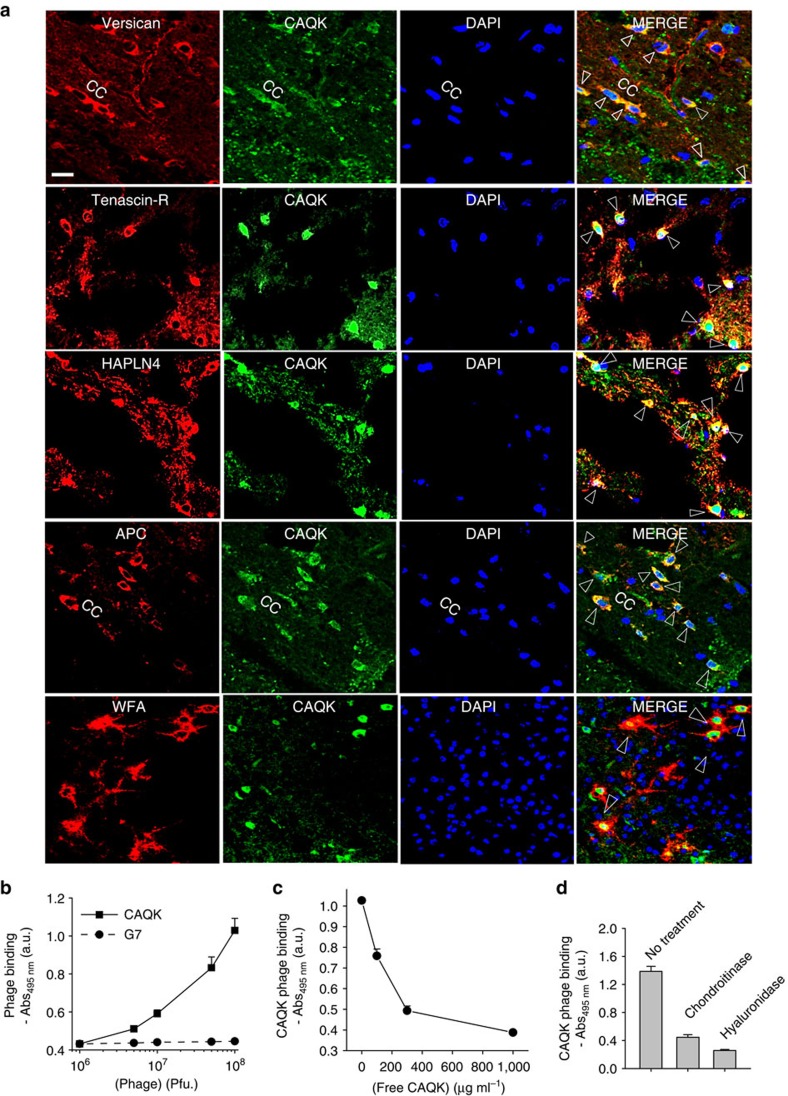
Figure 3. CAQK co-localizes with chondroitin sulfate in PBI.
(a) Immunofluorescence images of PBI sections showing the corpus callosum (CC) region. The sections were stained for versican, tenascin-R and the hyaluronan proteoglycan link protein, the oligodendrocyte marker (adenomatous polyposis coli (APC)), and Wisteria floribunda agglutinin (WFA; shown in red), FAM-CAQK (green) using anti-fluorescein antibody and counterstained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Shown are representative brain sections of injured hemisphere in a PBI mouse injected with FAM-CAQK 6 h after injury. Arrows show co-localization. Scale bar, 20 μm (b) Phage binding to ECM formed by U251 cells. The cells were gently dissociated and removed, and the remaining ECM was incubated with phage for 1 h at room temperature, and phage binding was detected following an ELISA protocol. CAQK phage showed higher binding to ECM than control phage. (c) Inhibition of CAQK phage binding to ECM by free CAQK peptide. (d) Phage binding to ECM is reduced on enzymatic digestion of ECM with chondroitinase ABC or hyaluronidase. Mean±s.e.m. Representative data shown in b–d is from three experimental repetitions each with three sample replicates.