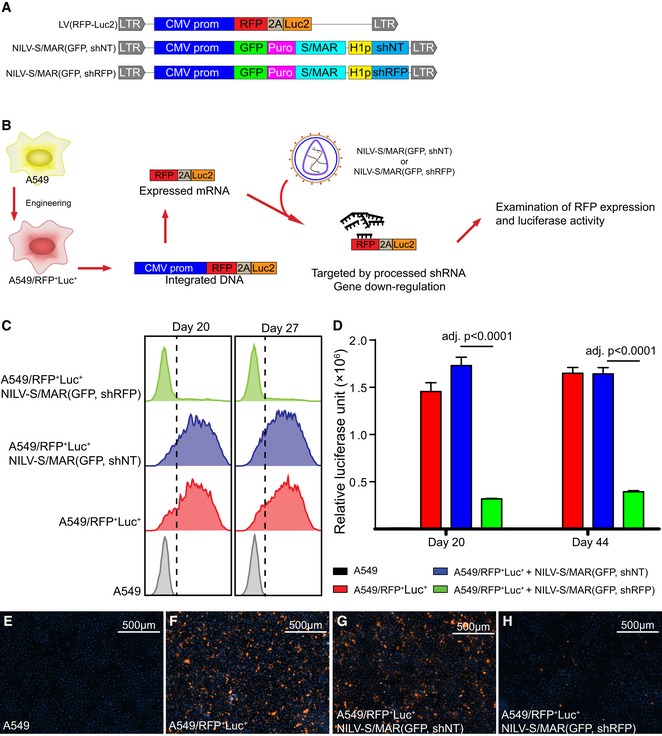
Figure 2. NILV‐S/MAR‐mediated gene knockdown.
-
ASchematic drawing of the lentiviral vectors used. Abbreviations as in Fig 1; RFP: red fluorescent protein; Luc2: codon‐optimized (for Homo sapiens) firefly luciferase; H1p: H1 RNA polymerase III promoter; shRFP: small hairpin RNA targeting the RFP transcript; shNT: small hairpin RNA with nontargeted control sequence.
-
BThe experimental setting for proof‐of‐concept experiment showing that a NILV‐S/MAR‐based vector can yield long‐term gene silencing.
-
CFlow cytometry histograms of RFP expression (x‐axis) of A549/RFP +Luc+ cells at days 20 and 27 after NILV‐S/MAR(GFP, shNT) or NILV‐S/MAR(GFP, shRFP) transduction.
-
DLuciferase activity of the A549/RFP +Luc+ cells at days 20 and 44 after NILV‐S/MAR(GFP, shNT) or NILV‐S/MAR(GFP, shRFP) transduction.
-
E–HRepresentative fluorescence microscopy images show the expression of RFP from either NILV‐S/MAR‐transduced or untransduced A549/RFP +Luc+ cells with cell nuclei stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). RFP signal (orange) was collected with a fixed exposure time (300 ms) for equal comparison.
