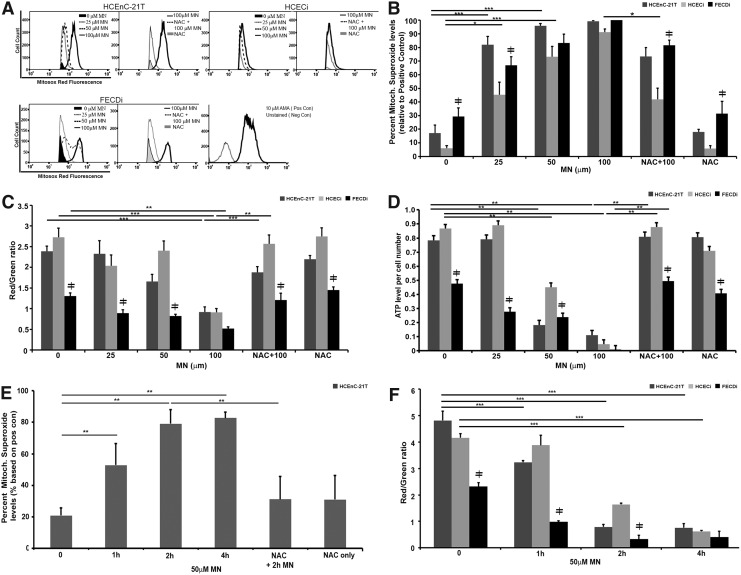
FIG. 3.
MN induced mitochondrial dysfunction. HCEnC, HCECi, and FECDi cells were exposed to MN in a dose-dependent manner for 1 h with or without NAC pretreatment and collected for measurement of mitochondrial ROS production by flow cytometry, ATP levels, and ΔΨm using the JC-1 assay, as described in the Materials and Methods section. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of mitochondrial O2•− production was measured by MitoSox Red fluorescence intensity and represented by histograms. MN increased MitoSOX Red intensity as early as 25 μM, while NAC pretreatment attenuated 100 μm MN-induced MitoSox Red intensity (n = 3); (B) Quantification of flow cytometry data. Results were normalized to the positive control, antimycin A-treated cells. (n = 3); (C) ATP levels were measured by a luminescence assay and normalized to cell number per sample (n = 6 in duplicate); (D) Represents ΔΨm levels as a ratio of red/green fluorescence, which is a change in JC-1 properties from aggregate to monomeric form in MN-treated cells (n = 4 in duplicate); (E) Time course analysis of mitochondrial O2•− levels with 50 μM MN in HCEnC-21T cells with or without NAC pretreatment (n = 4 in duplicate); (F) Time course analysis of MMP levels with 50 μM MN in all three cell lines (n = 4 in duplicate). Data are expressed as the mean ± SE. Two-way ANOVA was applied for statistical significance, comparing treated samples with untreated control (0). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ≠p < 0.05 FECDi versus HCEnC-21T and/or HCECi. ATP, adenosine triphosphate.